Figure 4.
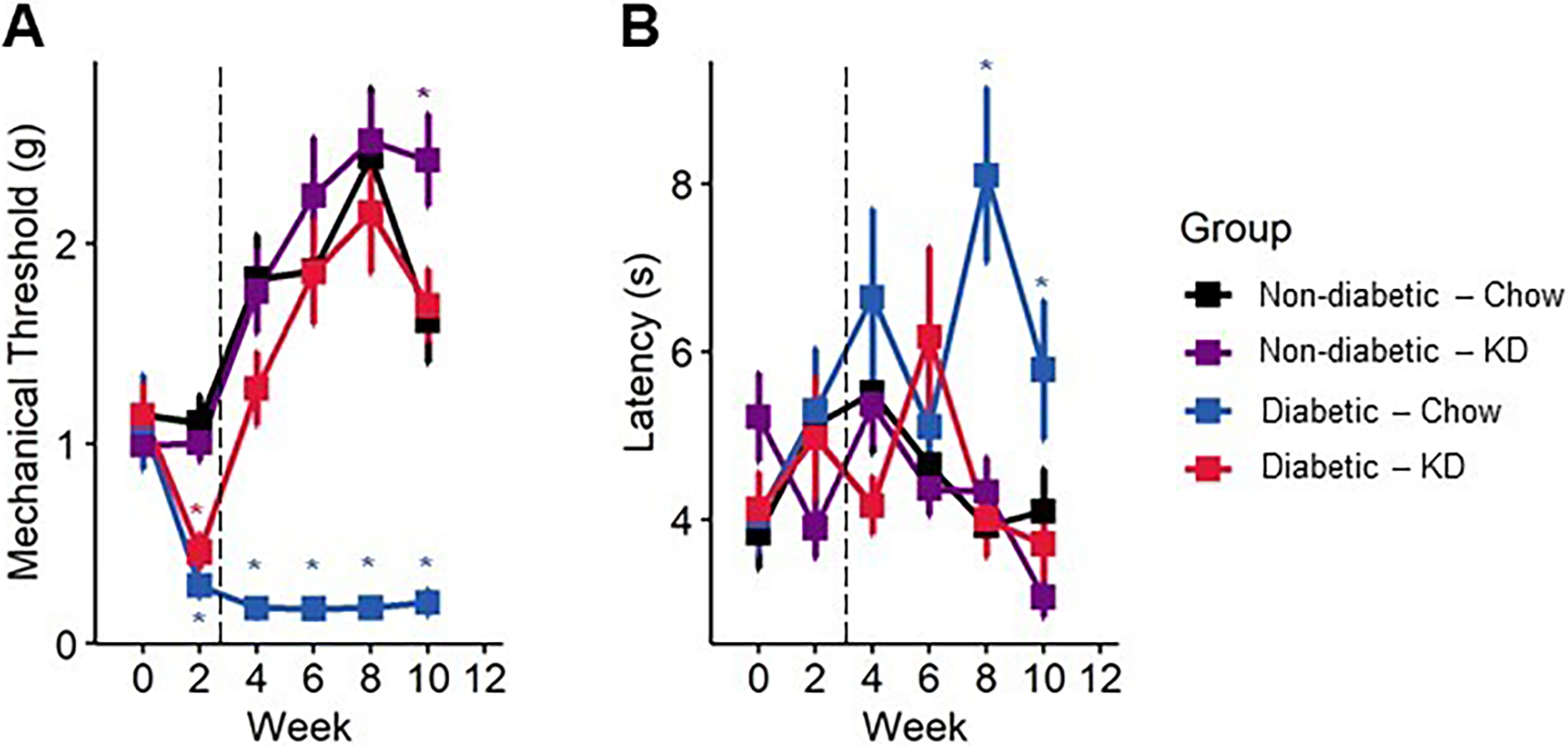
Sensory behavior in diabetic mice following administration of a ketogenic diet as a preventive intervention. (A) Diabetes induces a sharp, lasting decline in mechanical withdrawal thresholds as assessed by Von Frey filaments, indicative of mechanical allodynia. Within a week of administration of a ketogenic diet, diabetic mice returned to normal levels of mechanical sensitivity (n=7–12). (B) Diabetic mice slowly develop a delayed response to noxious heat stimuli, as assayed by radiant heat assay. The thermal hyporesponsiveness was prevented in diabetic mice fed a ketogenic diet (n=7–12). (A-B) Mixed-models ANOVA with repeated measures and Tukey’s post hoc test; * p < 0.05 compared to chow-fed non-diabetic mice.
