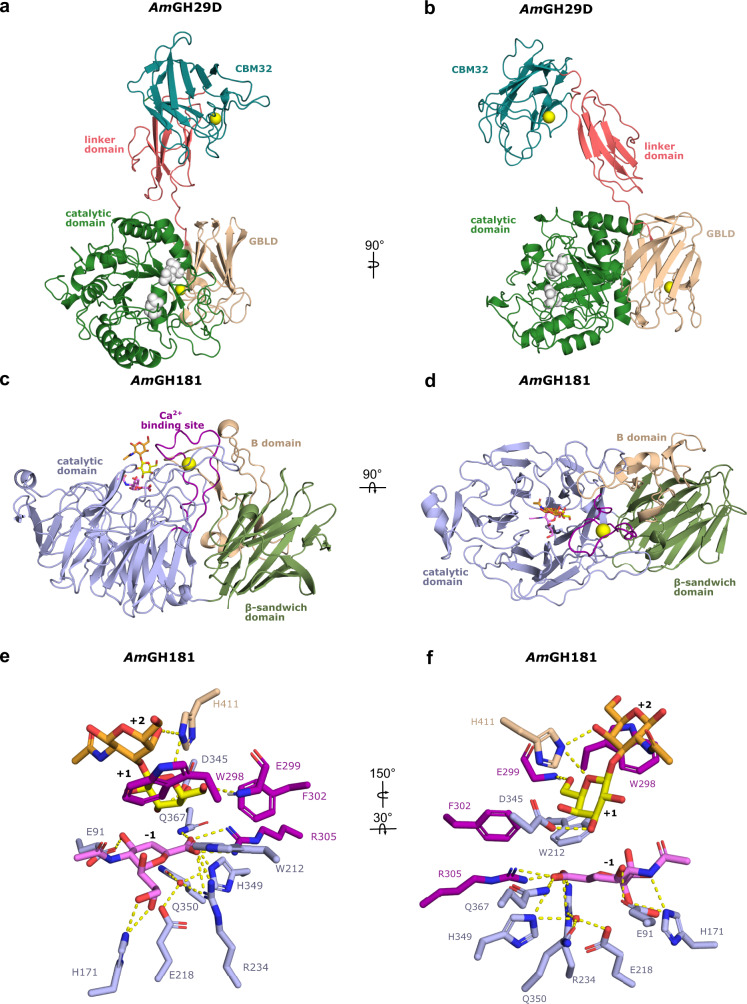
Fig. 3. The crystal structures of the AmGH29D fucosidase and AmGH181 sialidase from A. muciniphila.
a Overall structure of AmGH29D comprising a catalytic N-terminal (β/α)8 domain (amino acids 38-362), a predicted galactose binding like domain (GBLD, aa 363-489), a linker domain comprising two β-sheets formed by five antiparallel strands (aa 490-571) and a C-terminal CBM32 (aa 572-704). The inferred catalytic residues (white) and the bound Ca2+ ions (orange) are shown as spheres. b A 90° rotation of the view in a. c Overall structure of AmGH181, comprising an N-terminal 6-fold β-propeller catalytic domain (aa 23-281 and 307-384) with a Ca2+-binding domain formed by an extended loop between two inner β-strands in propeller blade 2 (aa 282-306). The Ca2+ (orange sphere) is assigned based on coordination geometry and distance. The catalytic domain is joint to a C-terminal β-sandwich CBM-like domain (residues 457-595) and an inserted B domain (aa 391-456) between the β-strands 1 (sheet I) and 2 (sheet II) of the CBM-like domain. d A 90° rotation of the view in c. e, f The active site of AmGH181 with the DANA inhibitor (subsite −1) and the T-antigen disaccharide bound at the +1 and +2 subsites in two different orientations. The same domain colours are used in panels c–f.