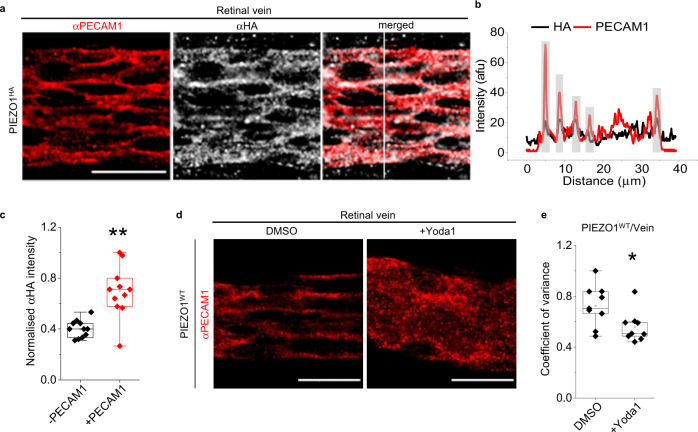
Fig. 2. Endogenous PIEZO1 is close to and can disrupt PECAM1 at cell-cell junctions.
a Images for retinal vein of PIEZO1HA mouse after immuno-staining with αPECAM1 (red) and αHA (grey). The image on the right side is a merged αPECAM1 and αHA image. Scale bar, 20 µm. b Line-intensity plot for the vertical scan line superimposed in the merged image of a. Grey highlighting indicates cell-cell junctions. c Box-plot quantification of image intensity for PIEZO1HA retinal veins stained with αHA antibody, shown in arbitrary fluorescence units (afu) normalised to the background measurements in the same afu. **P = 0.00127 for the comparison of the regions with (+) or without (−) PECAM1. Superimposed data points are average intensity of individual images (N = 11). Data are for n = 3 independent experiments. d Data obtained after WT mice were infused for 30 min with standard bath solution (SBS) containing DMSO (the solvent for Yoda1) or 3 µM Yoda1. Representative images of d retinal vein immuno-stained with αPECAM1 antibody. Scale bar, 20 µm. Box-plots e show coefficients of variance calculated from scan lines that were vertical to a blood vessel oriented from left to right (*P = 0.02728 for Yoda1 cf DMSO in vein). Lower variance indicates less organised structure. n = 3 independent experiments and 3 replicates were used in each case. Superimposed data points are the coefficient of variance for individual images (DMSO, N = 9 and +Yoda1, N = 9).