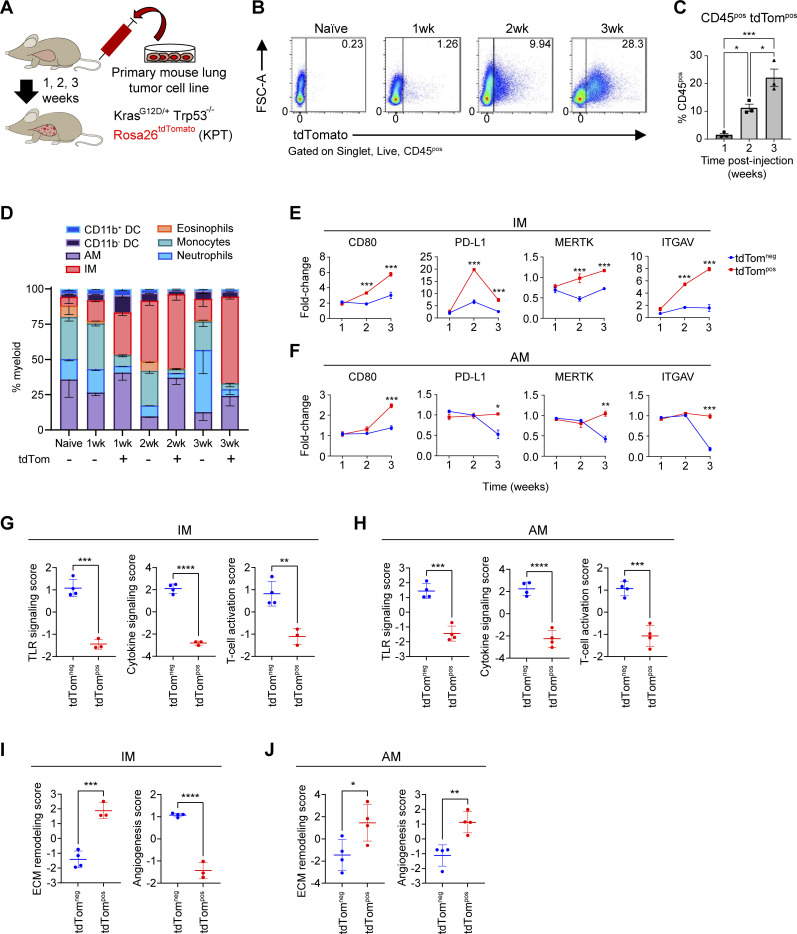
Figure 1.
TAMs have distinct phenotypes after phagocytosis in acute lung tumor mouse models. (A) Schematic of intravenous transplantation of a primary lung tumor cell line (KPT; SP110P) into recipient F1 C57BL/6J-129S1/Svlmj mice over a 3-wk time course. (B) Flow cytometry gating of CD45pos tdTompos and tdTomneg lung macrophages gated on cells at 1, 2, and 3 wk after i.v injection of KPT primary lung tumor cell line. (C) Ordinary one-way ANOVA (*, P ≤ 0.05; ***, P ≤ 0.001). Bar plots showing the percentage of CD45pos tdTompos cells in the acute lung tumor model after i.v. injection. (D) Myeloid cell composition within the tdTompos or tdTomneg immune cell fraction in naive and tumor-bearing mice. (E and F) Fold change MFI of immune-modulatory and phagocytosis cell surface markers on IMs (E) or AMs (F) relative to naive IMs or AMs, respectively. Unpaired t test (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001). (G–J) Pathway enrichment score of immune-activation gene modules (G and H) and tissue-reorganization gene modules (I and J) for tdTompos or tdTomneg IMs and AMs based on analysis of focused panels of Nanostring mRNA probes. Unpaired t test (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001; ****, P ≤ 0.0001). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments.