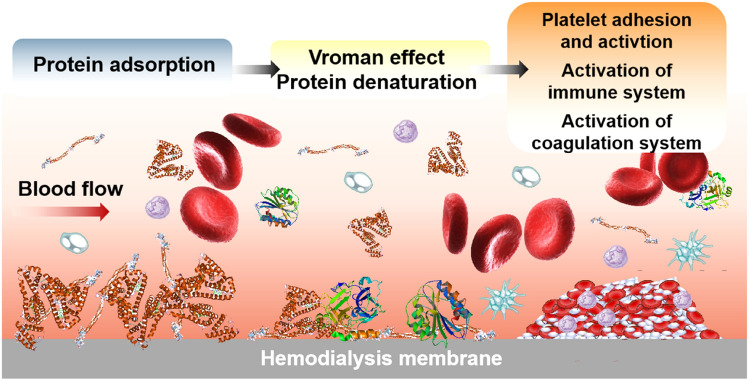
Fig. 3.
Protein adsorption process on the HFM surface. Small proteins that are present at higher concentrations and low surface affinity in blood, such as albumin, are rapidly and reversibly adsorbed and may subsequently be replaced by larger proteins with a higher surface affinity. The adsorbed proteins tend to maximize their footprint through conformational reorganization since surface-protein contact induces a gain in free energy. The adsorbed and denatured proteins trigger the activation of coagulation, immune and inflammatory responses at the HFM surface during dialysis