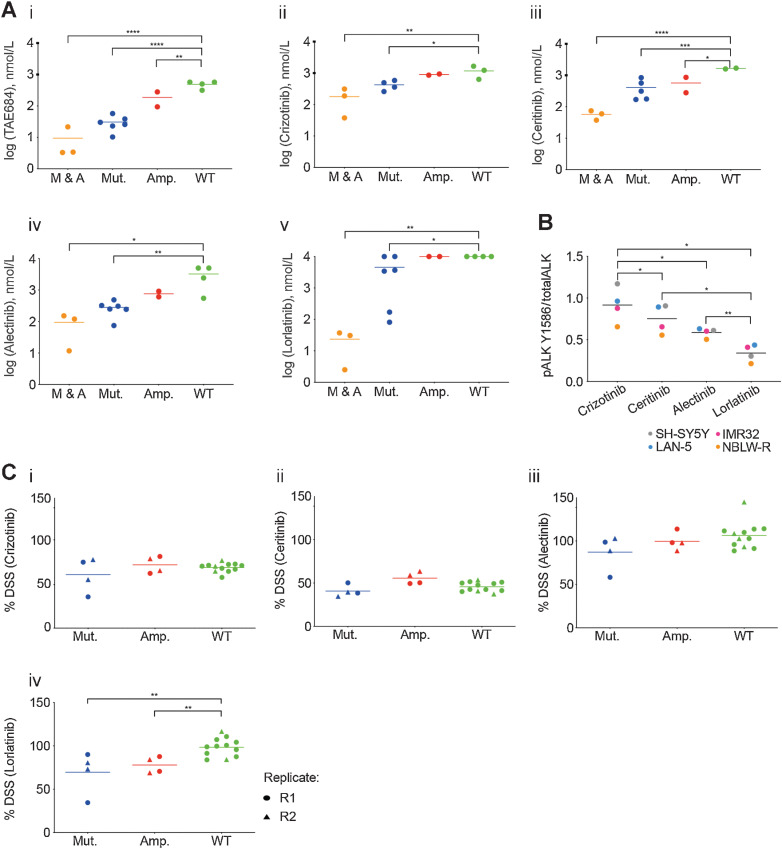
Figure 1.
Lorlatinib is the most potent ALK inhibitor tested across ALK-mutant or ALK-amplified neuroblastoma cell lines and PDTC ex vivo models. 72-hour GI50 values for ALK inhibitors. A, (i) TAE-684, (ii) crizotinib, (iii) ceritinib, (iv) alectinib, and (v) lorlatinib in a panel of neuroblastoma cell lines (M & A: mutant and amplified ALK; Mut.: mutant ALK; Amp.: amplified ALK; WT: wild-type ALK). Cell lines were grouped on the basis of the type of ALK alteration. Statistically significant differences were determined by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc tests and paired testing versus WT. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, 0.01; ***, 0.001; ****, 0.0001. B, Neuroblastoma cell lines treated with 20 nmol/L of indicated inhibitor for 3 hours, and lysates subjected to ALK immunoassay for total ALK and pY1586 ALK. Statistically significant differences determined by paired, two-tailed t test. *, P ≤ 0.05; **, 0.01; ***, 0.001. C, Study of cell viability by analysis of the DSS after treatment with (i) crizotinib, (ii) ceritinib, (iii) alectinib, or (iv) lorlatinib in ALK-mutant and -amplified PDTC models. R1: replicate 1; R2 replicate 2. Statistically significant differences determined by unpaired, two-tailed t test. **, P ≤ 0.01.