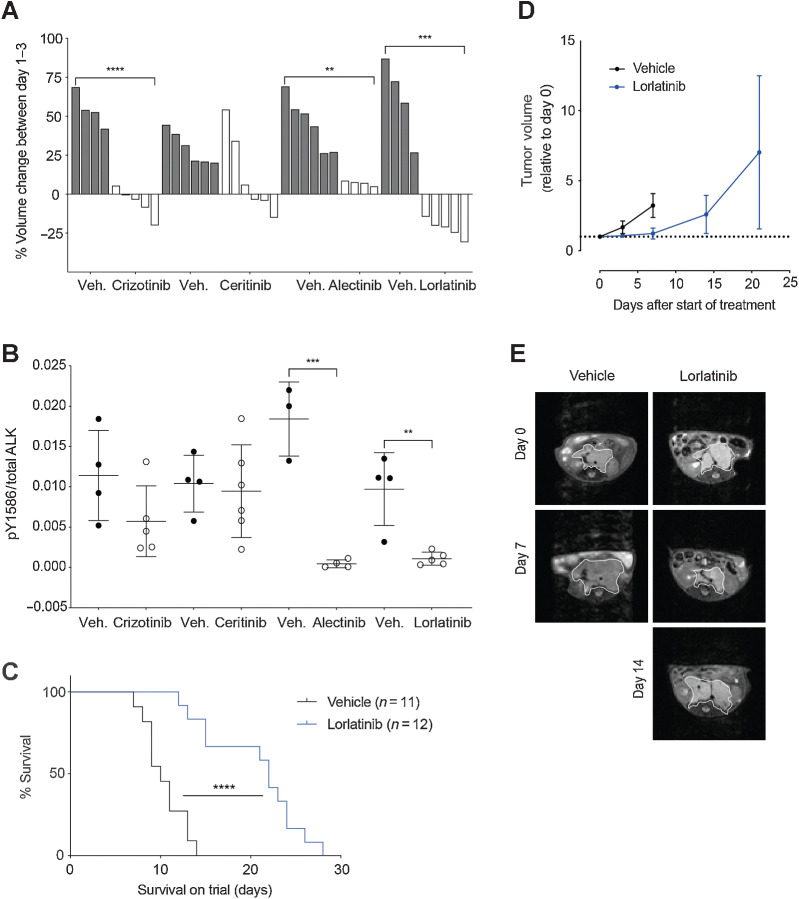
Figure 2.
Lorlatinib treatment of Th-ALKF1174L/MYCN tumor-bearing animals gives a survival advantage over vehicle control. A,In vivo analysis of a panel of ALK inhibitors including crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, and lorlatinib was carried out using the Th-ALKF1174L/MYCN model. Tumor-bearing Th-ALKF1174L/MYCN mice, were treated with the indicated inhibitor or its corresponding vehicle (veh.) over a 3-day interventional dosing schedule, and tumor volume change was monitored by MRI on day 0 and day 3. Each bar represents tumor volume change in an individual animal. Crizotinib versus vehicle ****, P < 0.0001. Alectinib versus vehicle **, P = 0.0021. Lorlatinib versus vehicle ***, P = 0.0002. B, Tumors from A were harvested for immunoassay testing of ALK and pY1586 ALK status. Alectinib versus vehicle ***, P = 0.0005. Lorlatinib versus vehicle **, P = 0.0037. C, Th-ALKF1174L/MYCN animals were treated with lorlatinib twice daily versus vehicle control to assess survival. ****, P < 0.0001 according to log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. D, Tumor volume was monitored by MRI. E, Representative abdominal MRI of an animal from the lorlatinib survival study versus vehicle control. Tumor outlined by white line.