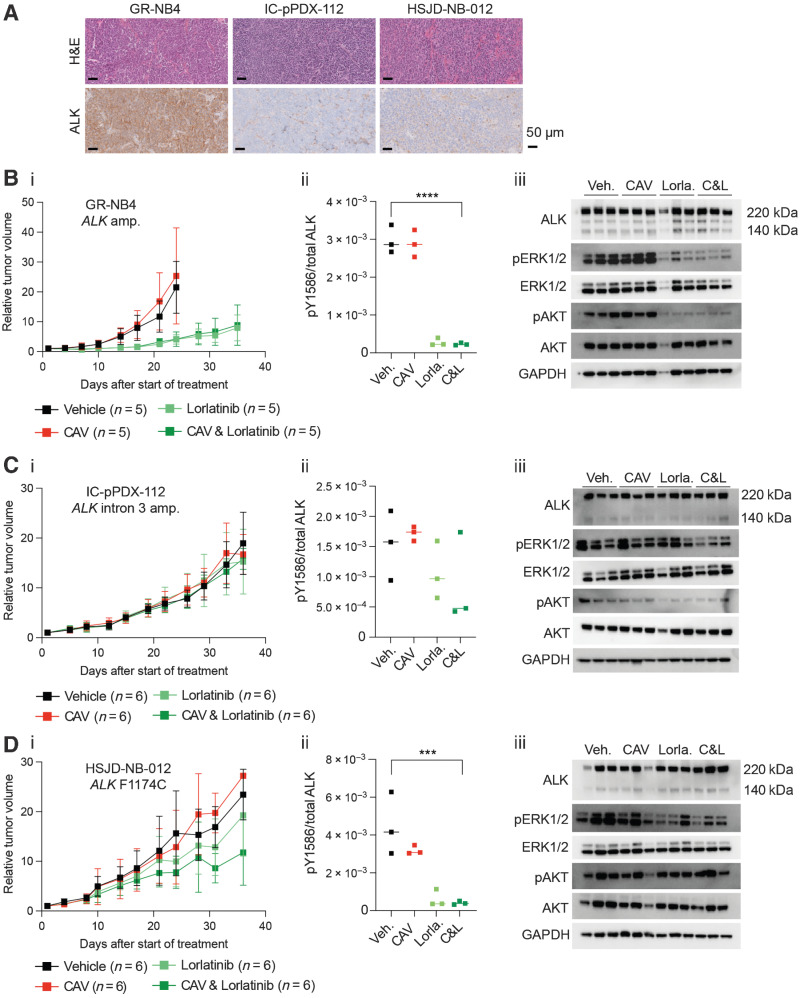
Figure 4.
High baseline in vivo expression of ALK determines sensitivity to lorlatinib in an ALK-amplified PDX neuroblastoma model. A, Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and ALK IHC staining of vehicle-treated tumors from indicated PDX models, treated for 3 days. GR-NB4 (B), IC-pPDX-112 (C), and HSJD-NB-012 (D) PDX models were treated with vehicle control, one dose of chemotherapy (CAV: cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and vincristine), continuous lorlatinib, or chemotherapy and continuous lorlatinib combination. (i) Tumor volumes were monitored during treatment. (ii) pY1586/total ALK measured by immunoassay in tumor lysates taken at the end of the experiment (mean of two technical replicates; Veh.: vehicle; Lorla.: lorlatinib; C&L: CAV and lorlatinib). One-way ANOVA: B.ii: P < 0.0001; C.ii: not significant; D.ii: P = 0.0010 (iii). Immunoblots of signaling pathways downstream of ALK from tumor lysates as per (ii).