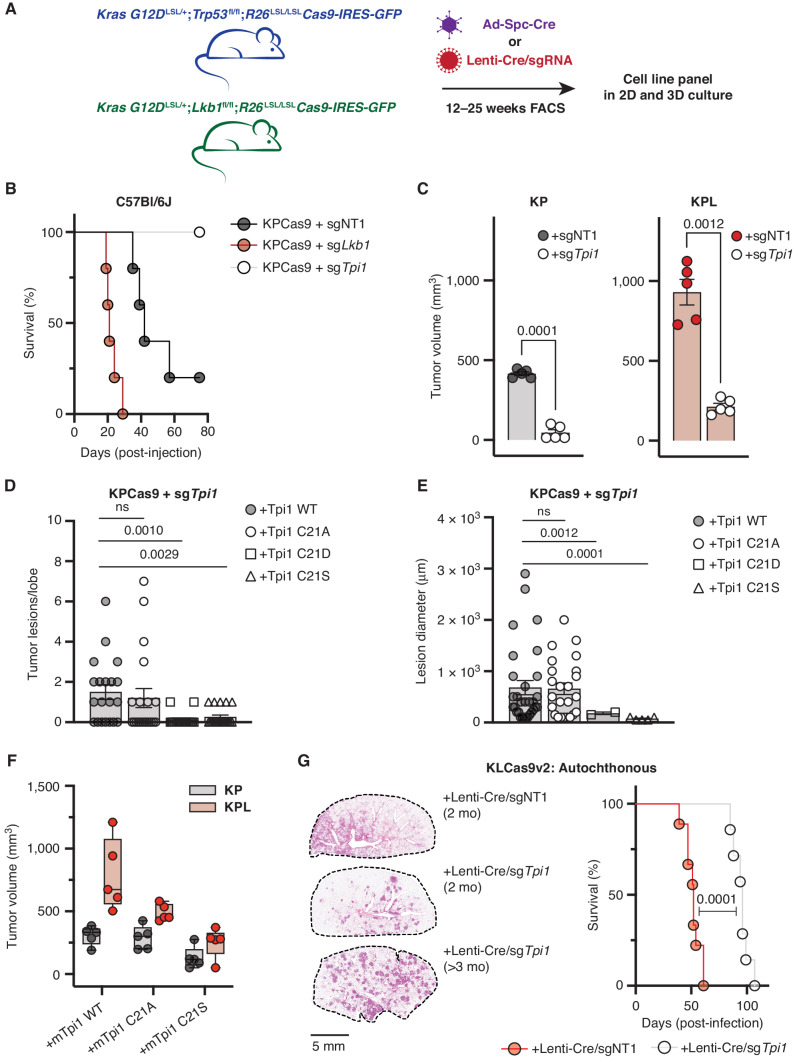
Figure 7.
TPI1 is required for tumor growth in KP and KPL LUAD models, and humanizing TPI1 regresses tumor growth and burden. A, Cartoon schematic depicting generated conditional genetic mouse models and subsequent derived tumor-derived cell lines. B, C57Bl/6J mouse survival following tail-vein injection of the KPCas9 cell line (BS7341) infected with lentiviruses encoding control or targeting sgRNAs (n = 5/group). C, Subcutaneous tumor growth of KP- or KPL-derived tumor cell lines (BS7432) infected with lentiviruses encoding control or targeting sgRNAs 30 days following engraftment in C57Bl/6J mice (n = 5/group); paired t test provided. D, Histogram quantifying tumor lesions per lobe in tail-vein-injected KPCas9 (BS7431) Tpi1 allelic variants in C57Bl/6J mice (n = 5/group) and reported as the mean (± SEM). Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed paired t test. ns, not significant. E, Histogram quantifying tumor lesion diameter in tail-vein-injected KPCas9 (BS7431) Tpi1 allelic variants in C57Bl/6J mice (n = 5/group) and reported as the mean (± SEM). Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed paired t test. F, Subcutaneous tumor growth of KPCas9-derived tumor cell line (BS7432) first infected with control or Lkb1-targeting guide RNA to produce isogenic KP and KPL, respectively. Derived lines were then infected with lentiviruses encoding Tpi1 sgRNA with subsequent lentiviral expression of transgenic guide RNA resistant mTpi1 WT, C21A, or C21S and measured 30 days following engraftment. Paired flank injections in C57Bl/6J mice were conducted (KP/KPL for each transgene) per mouse (n = 5/group). G, KLCas9v2 autochthonous tumor model survival following intratracheal administration of lentiviruses encoding Cre-recombinase and control (sgNT) or targeting (sgTpi1) sgRNAs (n = 12/group). Representative lung tumor burden in groups of mice at 8 weeks (sgNT and sgTpi1) and 14.5 weeks (sgTpi1) following intubation; histologic appearance of tumor lesions.