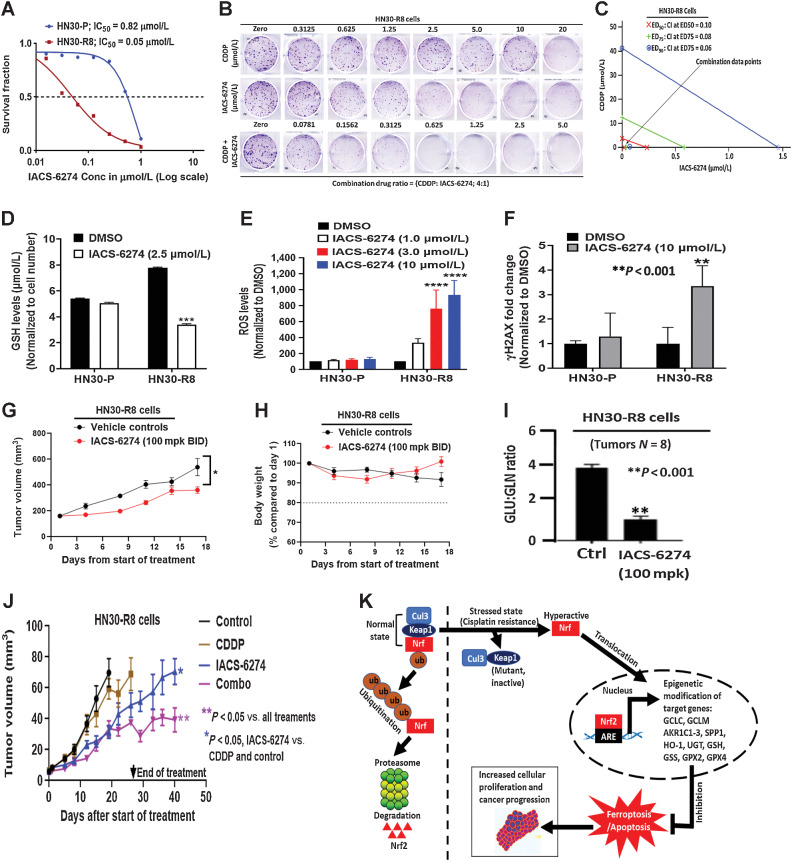
Figure 6.
Glutaminase synthase inhibition disrupts redox balance and overcomes acquired cisplatin resistance in vitro and in vivo. A, IC50 values obtained from clonogenic survival curves showing that HN30-R8 are more sensitive to the glutaminase synthase inhibitor (IACS-6274) in vitro compared with their parental HN30-P counterparts. B, Representative images of clonogenic survival assays in HN30-R8 cell lines treated with combination of CDDP and IACS-6274. C, Isobolograms assessed by Chou and Talalay CI indicate strong synergism with combination of CDDP and IACS-6274 in HN30-R8 cells. The CI < 1.0 indicates synergism. Addition of IACS-6274 to CDDP resulted in CI = 0.10 at the effective dose (ED50) that killed 50% of the cells following treatment with the two drugs. D, Reduced levels of GSH (***, P < 0.001) in HN30-R8 cells following treatment with IACS-6274. E, ROS levels are significantly elevated (****, P = 0.0001) after treatment with various doses of IACS-6274 in HN30-R8 compared with HN30-P cells in vitro. F, Treatment with IACS-6274 increases expression of the DNA damage response marker, H2AX, in HN30-R8 compared with HN30-P cells. Mice injected with HN30-R8 cells were treated with IACS-6274 as described in Methods. G, Single-agent IACS-6274 activity was observed with 100 mg/kg twice a day dosing regimen (*, P = 0.03 two-way ANOVA) and was well tolerated (H). Treatment with IACS-6274 for 8 hours decreases GLU/GLN ratio indicating target engagement with the dose used (I). Nude male mice were injected orally with the HN30-R8 CDDP-resistant cells and treated with vehicle control, CDDP, IACS-6274 alone and in combination with CDDP as described in Methods. J, IACS-6274 showed single agent activity, enhanced CDDP sensitivity, and decreased tumor growth. K, Proposed signaling model of acquired CDDP resistance in HNSCC. Under non-stressed conditions, KEAP1 directs ubiquitin-mediated degradation of NRF2 via proteasomes. Under oxidative stress generated by CDDP resistance, KEAP1 is mutated, NRF2 is stabilized and promotes transcription of ARE-containing genes associated with epigenetic modification of its downstream target genes. The hyperactivated NRF2 can protect the HNSCC cells from oxidative stress via suppression of ferroptotic and/or apoptotic cell death leading to enhanced cellular proliferation and accelerated tumor progression.