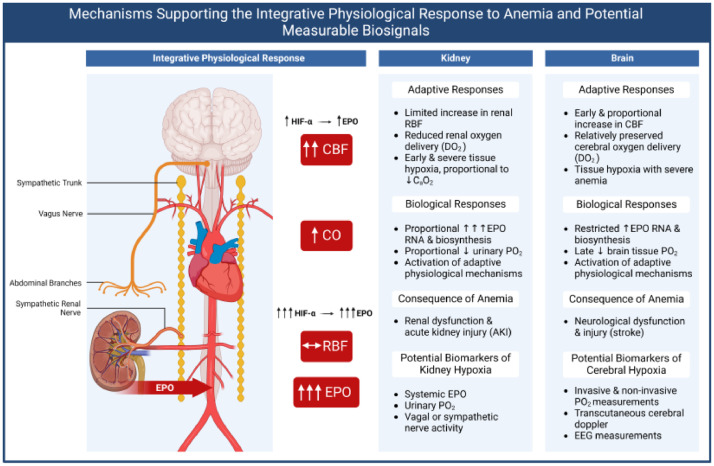
Figure 1.
Summary of integrative physiological responses to anemia and potential means of clinical assessment. Under anemic conditions, renal blood flow is maintained but associated oxygen delivery is decreased. This allows the kidney to sense decreases in blood oxygen content. Renal Erythropoietin (EPO) production is greatly stimulated at all levels of anemia in response to stabilization of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-alpha (HIF-α). The lack of increased Renal Blood Flow (RBF) makes the kidney susceptible to hypoxia and Acute Kidney Injury (AKI). By contrast, the brain is protected to an extent during anemia via an increase in cerebral blood flow, allowing maintenance of oxygen delivery in mild to moderate anemia. Brain tissue hypoxia in response to severe anemia is associated with increased HIFα and EPO expression and may contribute to neurological injury and stroke. Biomarkers to identify renal and brain hypoxia are listed. This figure was created in BioRender.com. CBF, Cerebral Blood Flow; CO, Cardiac Output; DO2, Oxygen Delivery; CaO2, Arterial Oxygen Content.