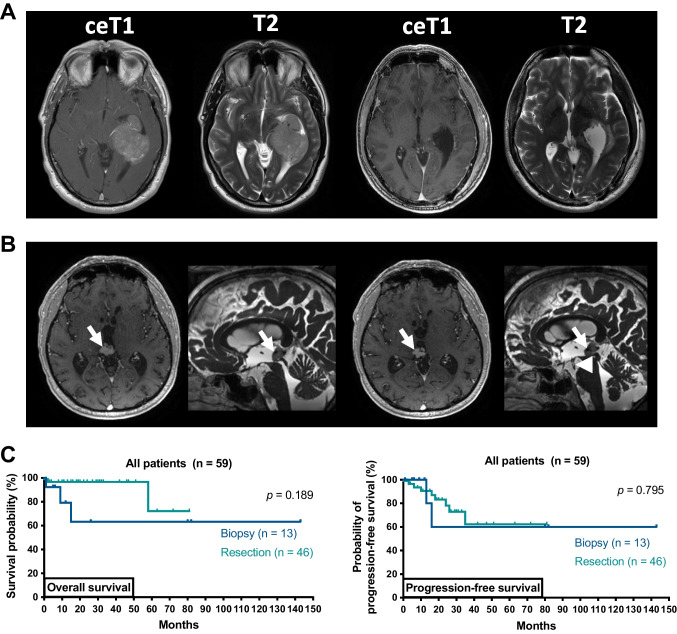
Fig. 3.
Outcome in patients depending on extent of resection. A Case example of a complete tumor resection: preoperative axial T1-weighted gadolinium enhanced and T2-weighted MRI showing an extensive contrast-enhancing (ce) lesion in the left inferior horn and atrium of the lateral ventricle consistent with an intraventricular meningioma (left). The patient underwent tumor resection via a parietal transcortical approach and complete resection was achieved (i.e., 100% of ce tumor volume, right). Histopathological examination confirmed meningioma and the patient was discharged without new focal neurologic deficits. B Case example of a stereotactic biopsy combined with internal shunt implantation: preoperative axial and sagittal MRI demonstrating a nodular lesion in the pineal region (arrows) with beginning obstructive hydrocephalus (left). Postoperative imaging demonstrating the internal shunt catheter (arrowhead) perforating the floor of the third ventricle and connecting the third ventricle with the basal cisterns (right). Histopathological findings demonstrated a papillary tumor of the pineal gland, and the patient was treated with radiotherapy. C Kaplan–Meier estimates of overall survival and radiographic progression-free survival in patients receiving biopsy (n = 13, dark blue) versus patients receiving tumor resection (n = 46, light blue). Tick marks indicate censored patients. Abbreviations: ceT1 T1-weighted gadolinium enhanced sequences, T2 T2-weighted sequences