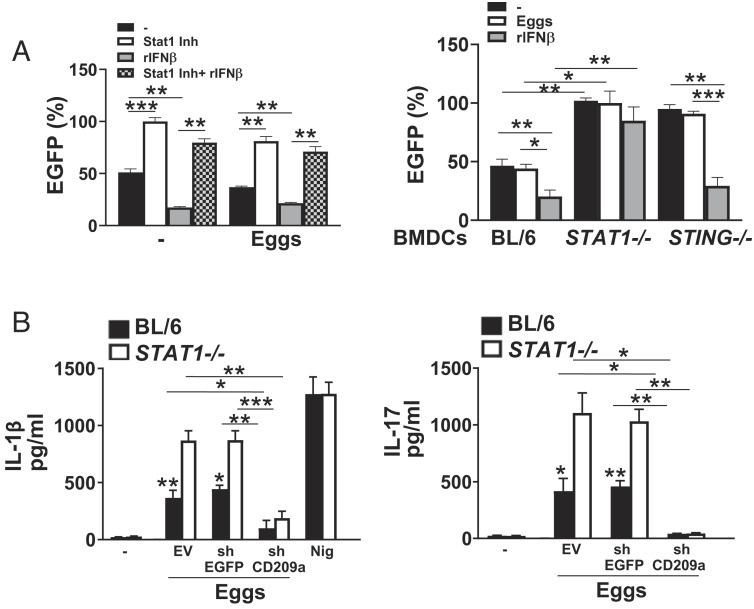
Fig. 5.
IFN-I suppresses CD209a promoter activity via STAT1. (A) BMDCs from BL/6 mice were transduced with EV (not shown) or CD209a-promoter-EGFP and then pretreated with 5 μg of STAT1 inhibitor fludarabine phosphate for 1 h alone or before stimulating with 2,000 units/mL rIFNβ. Some cells were stimulated with just rIFNβ. The cells were then stimulated with 100 eggs for 24 h. EGFP levels were measured using a plate reader. Data presented as the percentage of EGFP, with EGFP levels in STAT1 inhibitor (Inh)-treated BMDCs being set at 100%. (Left). BMDCs from BL/6, STAT1−/−, and STING−/− mice were transduced with EV (not shown) or CD209a-promoter-EGFP and then pretreated with 2,000 units/mL rIFNβ before stimulation with 100 eggs for 24 h (Right). Data presented as the percentage of EGFP, with EGFP levels in untreated STAT1−/− BMDCs being set at 100%. (B) BMDCs from BL/6 and STAT1−/− mice were transduced with EV or CD209a-promoter-EGFP before stimulation with 100 eggs for 24 h. IL-1β (Left) and IL-17 (Right) in supernatants were assessed by ELISA. For the purpose of measuring IFNβ and IL-1β, cultures proceeded for 24 h, and for IL-17, cultures also included CD4 T cells and proceeded for 72 h. Bars represent the mean ± SD cytokine levels of three biological replicates from one representative experiment of three with similar results. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.005, ***P ≤ 0.0005, ns: not significant.