FIGURE 3.
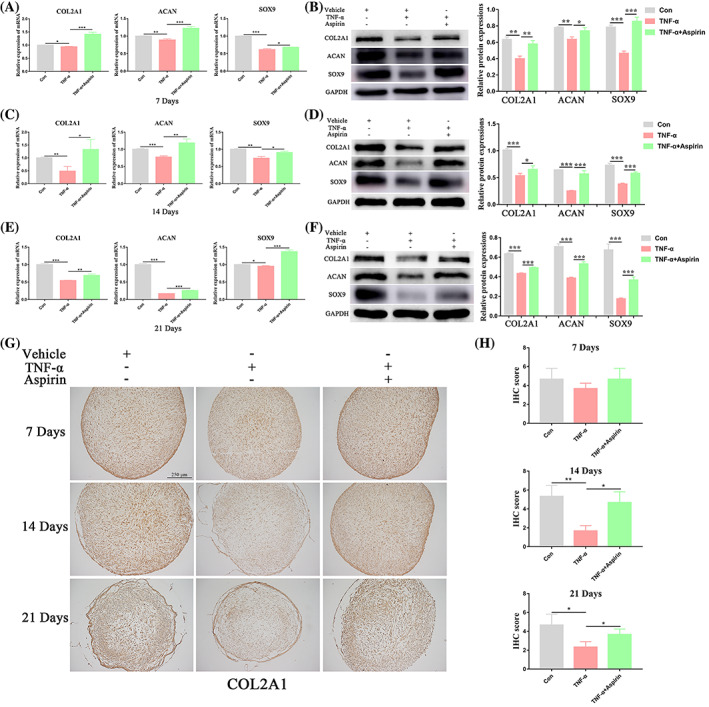
Aspirin reverses TNF‐α‐inhibited chondrogenic markers expression during chondrogenesis of BMMSCs. (A, B) Relative mRNA and protein expression levels of chondrogenic markers (COL2A1, ACAN, and SOX9) were measured in BMMSCs treated with or without TNF‐α and aspirin for 7 days by qRT‐PCR and western blot analyses, respectively. (C, D) Relative mRNA and protein expression levels of chondrogenic markers (COL2A1, ACAN, and SOX9) were measured in BMMSCs treated with or without TNF‐α and aspirin for 14 days by qRT‐PCR and western blot analyses, respectively. (E, F) Relative mRNA and protein expression levels of chondrogenic markers (COL2A1, ACAN, and SOX9) were measured in BMMSCs treated with or without TNF‐α and aspirin for 21 days by qRT‐PCR and western blot analyses, respectively. (G) IHC staining of COL2A1 in cartilage pellets cultured under different treatment conditions for 7, 14, and 21 days. (H) Quantification of the COL2A1 IHC staining data. Data in (A), (C), (E), and (H) are given as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ACAN, aggrecan; COL2A1, collagen type II alpha 1 chain; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde‐3‐phosphate dehydrogenase; SOX9, SRY‐box transcription factor 9. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Scale bars: 250 μm
