FIGURE 3.
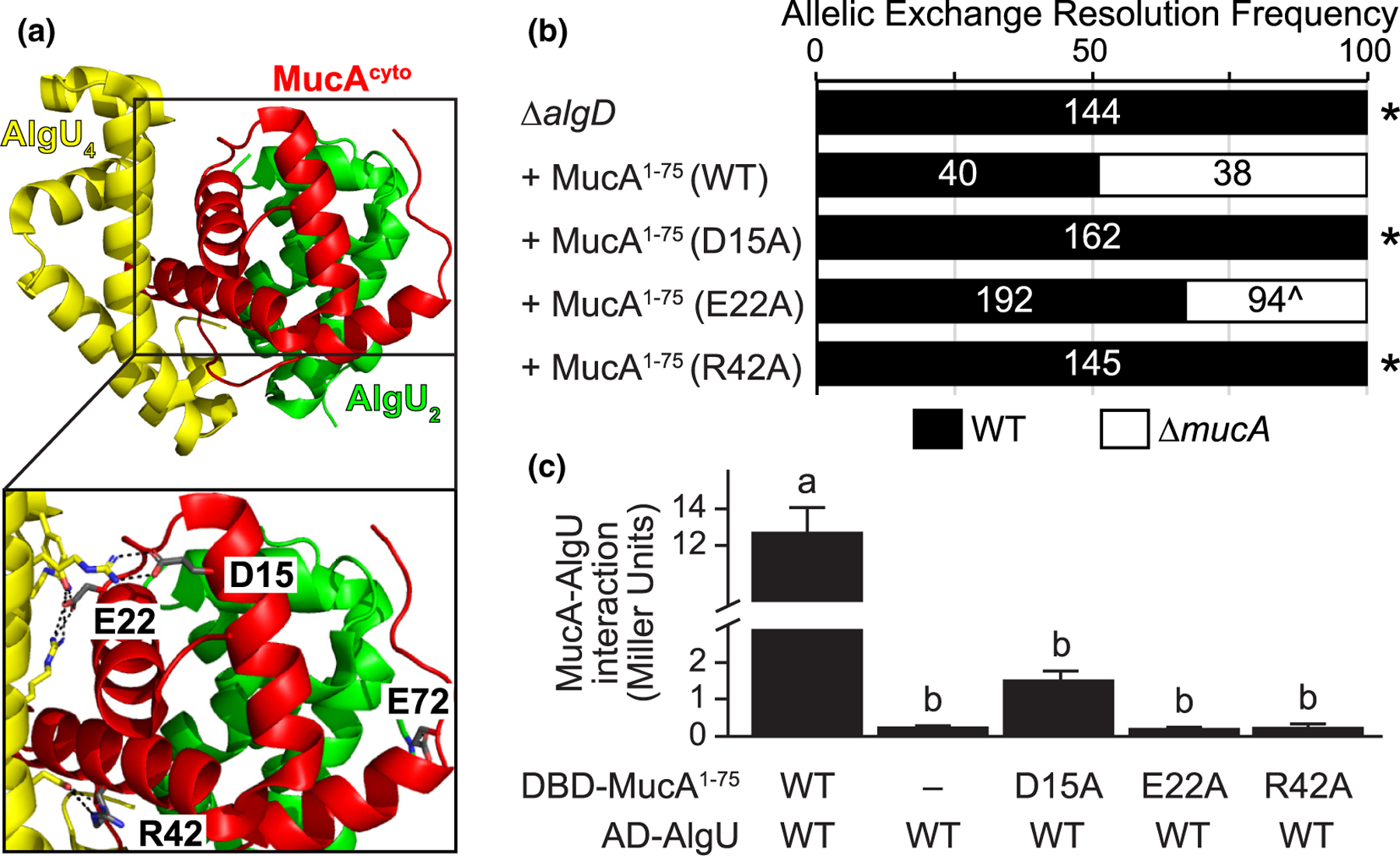
The physical interaction of MucA and AlgU is required for survival. (a) Four residues of MucA make greater than one predicted hydrogen bond with AlgU. The MucA-AlgU co-crystal structure (PDB 6IN7; Li et al., 2019) with the cytosolic domain of MucA (aa 1–78; red) and Regions 2 and 4 of AlgU (green, AlgU2; yellow, AlgU4) is shown. The residues of MucA that are predicted to make more than one hydrogen bond with AlgU (grey) are labeled in the inset. Black dotted lines, predicted hydrogen bonds; red atoms, oxygen; blue atoms, nitrogen. (b) Frequency of observed isolates resolving to the endogenous mucA allele (WT, black) or the deletion allele (∆mucA, white) in the allelic exchange assay, using PAO1 ∆algD attTn7::PalgU-mucA, where mucA encodes for the indicated substitution. Super-imposed on the bars are the number of isolates that were tested in each category. Asterisk, p < .0001; Fisher’s exact test. Caret, slower growing isolates. (c) Substitution of MucA residues at its interface with AlgU abolishes their binding via yeast two-hybrid. The first 75 residues of MucA were fused to the Gal4 DNA-binding domain (DBD-MucA1–75) and AlgU was fused to the Gal4 activation domain (AD-AlgU). Interaction of MucA and AlgU led to lacZ expression. Beta-galactosidase activity (in Miller units) was used as a proxy for the protein interaction strength. WT, wild-type protein sequence; −, no fusion protein included; hash, broken y-axis; error bars, SEM (N = 3); letters, statistical groupings (p < .01; biological triplicate with technical quadruplicates; ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD)
