FIGURE 4.
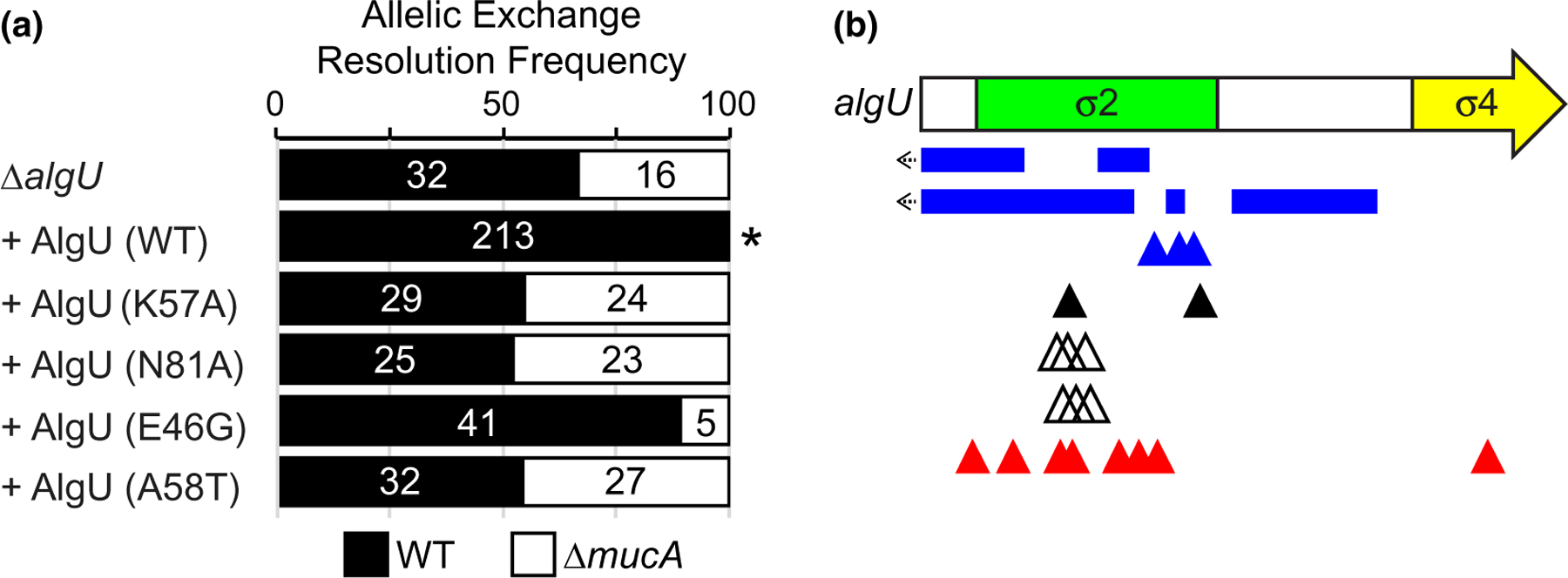
Mutations in AlgU can suppress mucA essentiality. (a) Frequency of observed isolates resolving to the endogenous mucA allele (WT, black) or the deletion allele (∆mucA, white) in the allelic exchange assay, using PAO1 ∆algU attTn7::PalgU-algU, where algU encodes for the indicated substitution. Super-imposed on the bars are the number of isolates that were tested in each category. Asterisk, p < .0001; Fisher’s exact test. (b) Schematic of mutations seen in revertants that could grow in the absence of mucA. Revertants were selected by growing PAO1 ∆mucA attTn7::PrhaBAD-mucA on media lacking rhamnose. Blue rectangles, multi-base pair deletions; left arrow, deletion extends into the promoter; blue triangles, single base pair deletions; black triangles, nonsense mutations; white triangles, duplications resulting in 3 or 4 amino acid insertions; red triangles, missense mutations. See Table S2 for a full description of the algU mutations
