FIGURE 5.
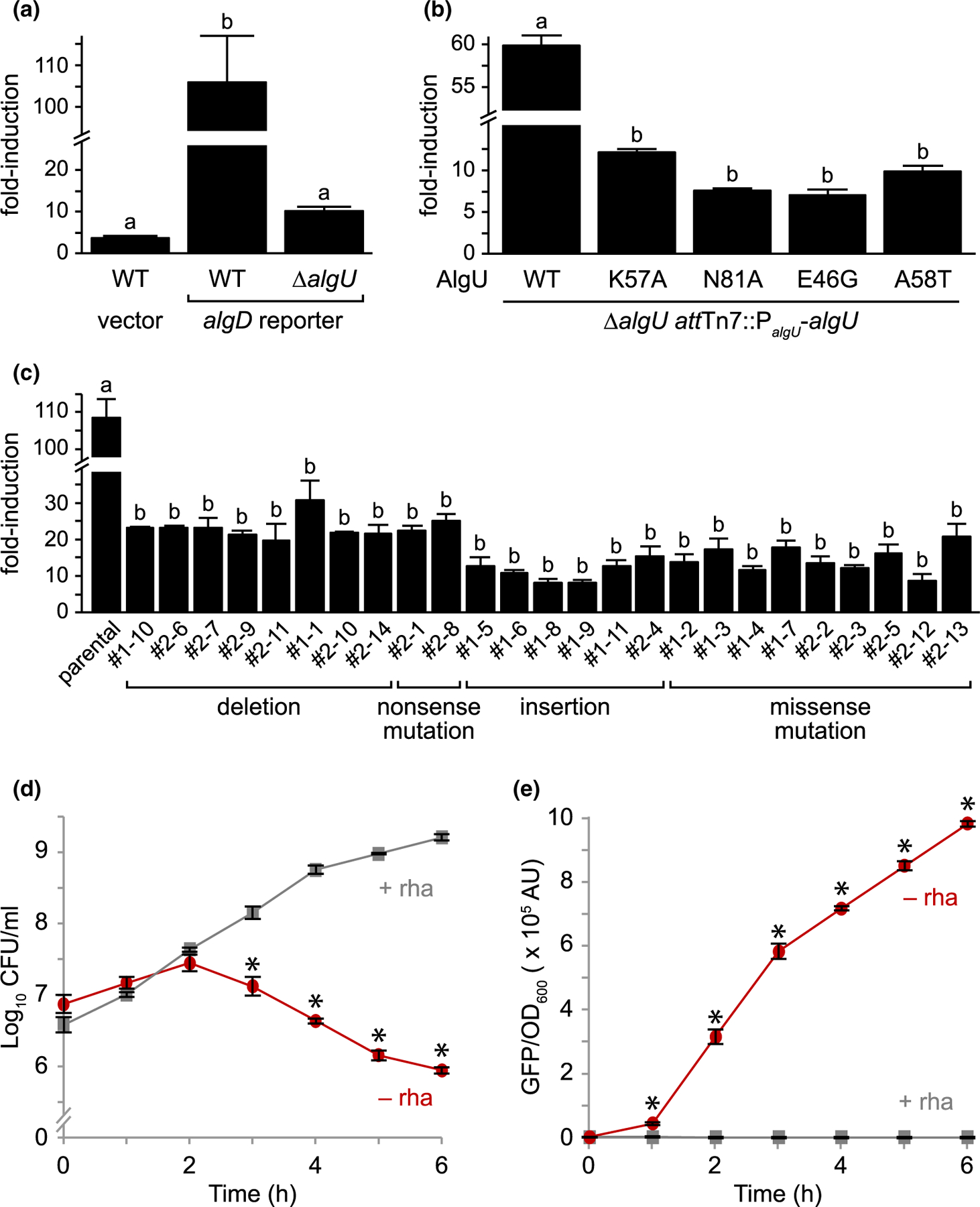
AlgU mutants that suppress mucA essentiality have decreased activity. (a) Fold-induction of GFP in PAO1 wild-type (WT) and ∆algU carrying a plasmid with either a promoter-less gfp (vector) or a gfp driven by the algD promoter (algD reporter), which is positively regulated by AlgU, after a 2h D-cycloserine treatment to activate envelope stress. GFP fluorescence was normalized to cell density and was then divided by the signal from untreated cells to determine the fold-induction. Hash, broken y-axis; error bars, SEM (N = 3); letters, statistical groupings (p < .01; biological triplicate with technical quadruplicates; ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD). (b) Fold-induction of GFP in PAO1 ∆algU attTn7::PalgU-algU, where algU encodes for the indicated substitution. The experiment and statistics are as described in (a). WT, the wild-type AlgU sequence. (c) Fold-induction of GFP in the revertants isolated from PAO1 ∆mucA attTn7::PrhaBAD-mucA (parental) that can grow in the absence of MucA. The experiment and statistics are as described in (a), except all cells were grown in the presence of 0.05% rhamnose to allow for comparison to the parental strain, which grows only in the presence of rhamnose. The isolate identification numbers are shown and are grouped based on their algU mutation. (d) Viable colony counts of PAO1 ∆mucA attTn7::PrhaBAD-mucA carrying the algD reporter over time in LB with (+ rha; gray squares) or without (− rha; red circles) 0.05% rhamnose. Hash, broken y-axis; error bars, SEM (N = 3). Asterisk, statistically different from that at the same time point grown in the presence of rhamnose (p < .01, N = 3, mixed model ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni test). (e) Normalized GFP fluorescence of the samples in (d). GFP fluorescence was normalized to cell density. The statistical analysis is as described in (d)
