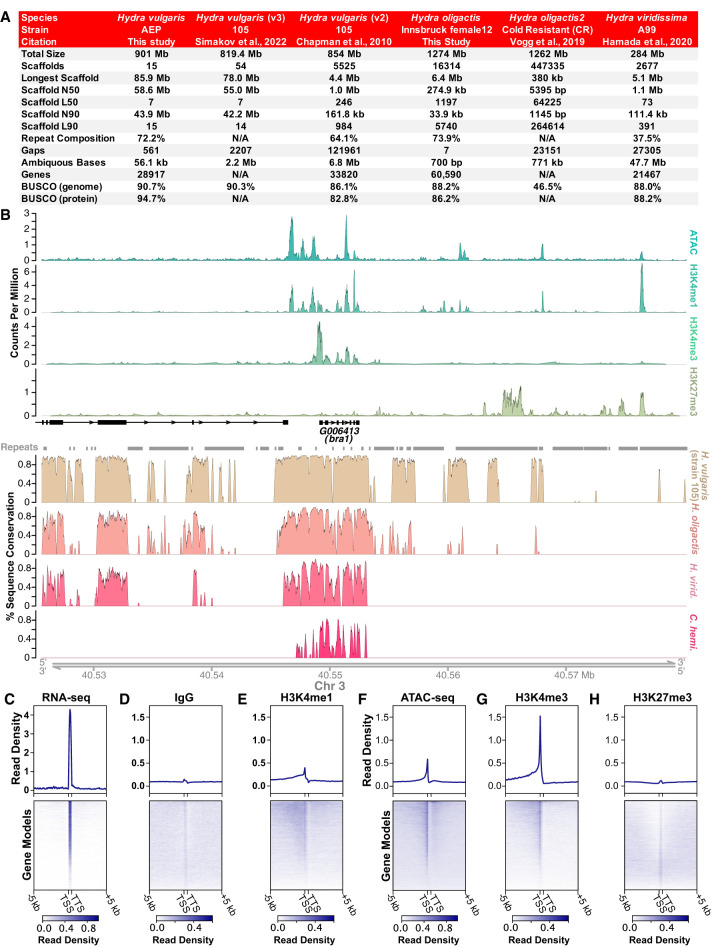
Figure 1.
New genome assemblies provide improved resources for Hydra molecular biology research. (A) The Hydra vulgaris strain AEP and Hydra oligactis genome assemblies presented in this study are marked improvements on the previously available reference genomes for their respective species. (B) Representative plot of CUT&Tag, ATAC-seq, and genomic conservation tracks centered on the hybra1 gene (Technau and Bode 1999). For the sequencing data, each track represents the signal from pooled biological replicates for the specified library type. A plot of the same locus that includes separate tracks for each CUT&Tag and ATAC-seq biological replicate is presented in Supplemental Figure S4. (C–H) Read distribution for sequencing data centered on AEP assembly gene models. (C) Whole-animal RNA-seq data are strongly enriched in predicted coding sequences. (D) Control IgG CUT&Tag reads show minimal enrichment in or around genes. (E) H3K4me1 is enriched in promoter-proximal regions, but only weakly enriched at transcription start site (TSS). (F) ATAC-seq is enriched at TSS, but also shows some enrichment in more distal regions, likely because ATAC-seq targets both promoters and enhancers. (G) H3K4me3 is strongly enriched at the TSS. (H) H3K27me3 shows minimal or no enrichment near transcribed genes. (TTS) Transcription termination site.