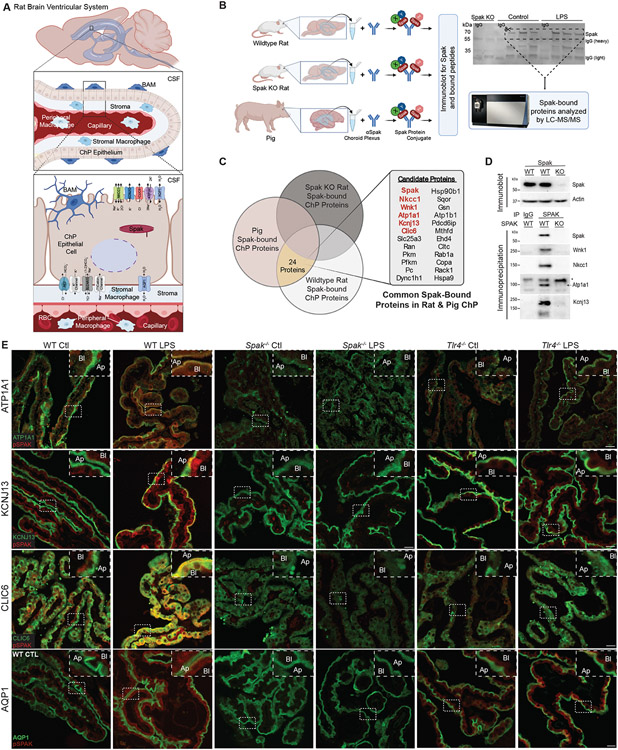
Figure 3. SPAK kinase is a regulatory scaffold for an apically-localized multi-ion transporter complex in ChP epithelial cells.
(A) Schematic illustrating the rat ventricular system and ChP, highlighting important ion transporters and channels in the apical and basolateral membranes of the ChP epithelium. BAM, border-associated macrophage; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; RBC, red blood cell. (B, left) Illustration of SPAK immunoprecipitation and LC-MS/MS analysis of SPAK-interacting proteins detected in the micro-dissected ChP of Spak+/+ and Spak−/− rats, and wildtype pig (see Methods). (B, right) Western blot of SPAK, illustrating removal of gel lanes (area of the dashed box) corresponding to SPAK/SPAK-associated proteins for analysis with LC-MS/MS. (C) Identification of 24 highly SPAK-bound polypeptides, shared between Spak+/+ rats and wild-type pig ChP, and absent from immunoprecipitates from lysates of Spak−/− rat ChP. (D) Immunoblot of SPAK (upper blot; beta-actin, loading control) and (lower blots) co-immunoprecipitations of SPAK with LC-MS/MS-identified SPAK-bound proteins WNK1, NKCC1, ATP1A1 (*non-specific band), and KCNJ13 (SDS-resistant tetramer shown) in Spak+/+ and Spak−/− rat ChP. (E) Representative IHC co-staining of pSPAK (red) with ATP1A1 (green, top row), KCNJ13 (green, second row), CLIC6 (green, third row), and AQP1 (green, last row) in ChP of WT, Spak−/−, and Tlr4−/− animals +/− LPS treatment (n=6 ChP per genotype, 3 animals per condition). Insets show magnification; apical membrane (Ap), basolateral membrane (Bl) of the choroid plexus. 40x, Scale bars 25 μm.