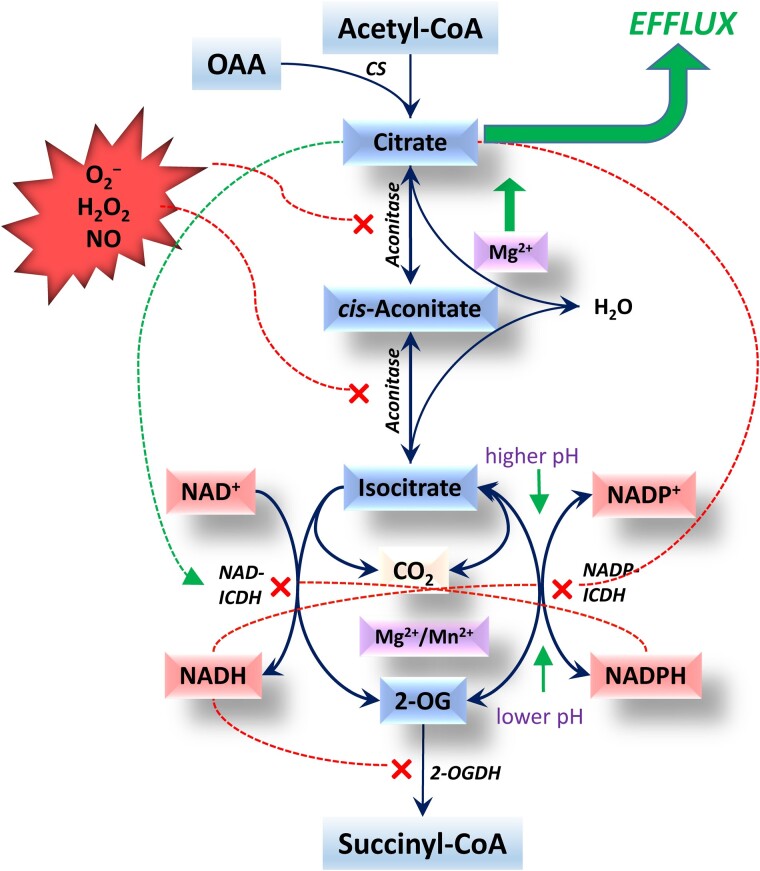
Figure 2.
TCA branch of the TCA cycle and its regulation. Superoxide anion (O2−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and nitric oxide (NO) inhibit aconitase via interaction with its iron–sulfur cluster. The irreversible NAD-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase (NAD-ICDH) and the reversible NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP-ICDH) constitute the substrate cycle responding to the changes in redox levels of NAD and NADP. NADH inhibits both enzymes, NADPH inhibits NAD-ICDH and stimulates the reverse reaction of NADP-ICDH, and citrate stimulates NAD-ICDH and inhibits NADP-ICDH. Mg2+ displaces the equilibrium of aconitase toward citrate and activates both ICDHs (also Mn2+). The inhibition of aconitase and both ICDHs and stimulation of the reverse reaction of NADP-ICDH result in the efflux of citrate from mitochondria. CS, citrate synthase; OAA, oxaloacetate; 2-OG, 2-oxoglutarate; 2-OGDH, 2-oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex. The blue lines indicate biochemical reactions, the red dotted lines indicate the enzyme inhibition, and the green dotted line shows the activation of NAD-ICDH by citrate.