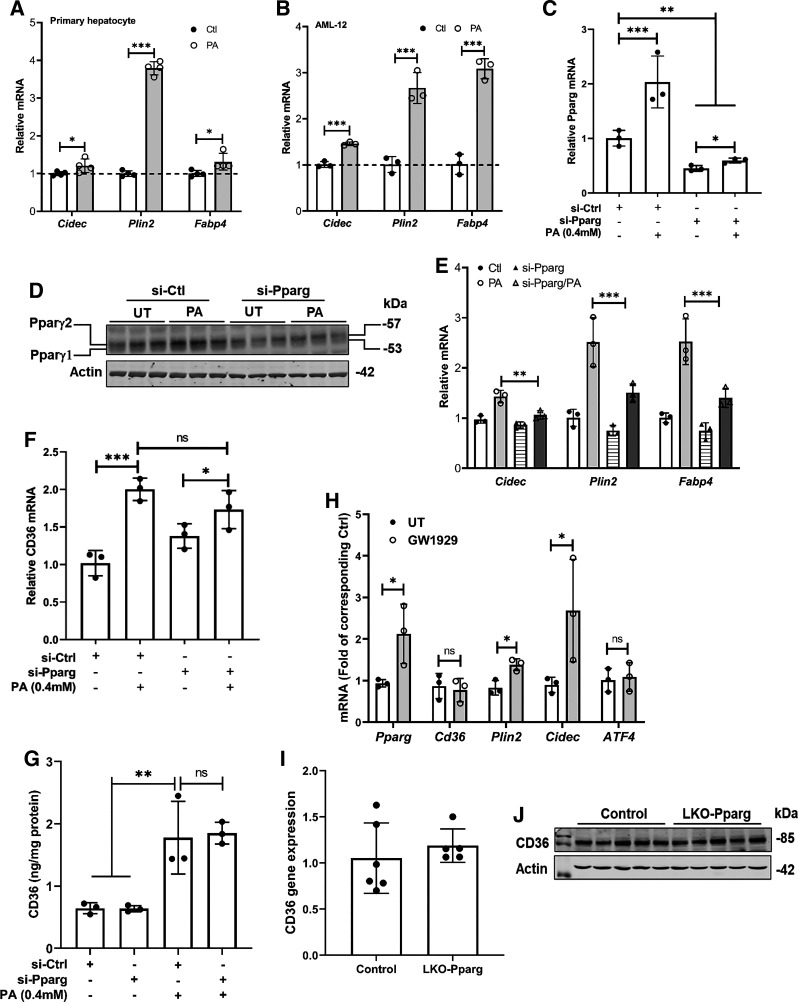
Figure 2.
Palmitate-induced CD36 upregulation is PPARγ-independent in hepatocytes. Primary mouse hepatocytes (A) and AML-12 cells (B) were treated with palmitate at 0.6 mM and 0.4 mM, respectively, for 16 h. PPARγ transactivation was determined by detecting its downstream target genes using real-time-qPCR. Data are expressed as means ± SD, n = 3 or 4 separate experiments. Student’s t test was used for statistical evaluation (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001). AML-12 cells were transfected with either scramble siRNA (si-Ctrl) or Pparg siRNA (si-Pparg) for 24 h before palmitate exposure (0.4 mM) for 16 h. Pparg expression (C and D), transactivation (E), and CD36 (F and G) expression were determined by real-time qPCR, Western blotting, and ELISA, and data were expressed as means ± SD, n = 3 separate experiments. Student's t test was used for statistical evaluation (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). H: AML-12 cells were treated with PPARγ agonist, GW1929 (10 µM), for 16 h. PPARγ transactivation was determined by detecting its downstream target genes using real-time qPCR. Data are expressed as means ± SD, n = 3 separate experiments. Student’s t test was used for statistical evaluation (*P < 0.05). I and J: total RNA was extracted from the liver tissues of control and hepatocyte-specific Pparg knockout (LKO-Pparg) mice and subjected to real-time qPCR for CD36 gene expression. Data are expressed as means ± SD (n = 5 or 6 mice/group). CD36, cluster of differentiation 36; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ.