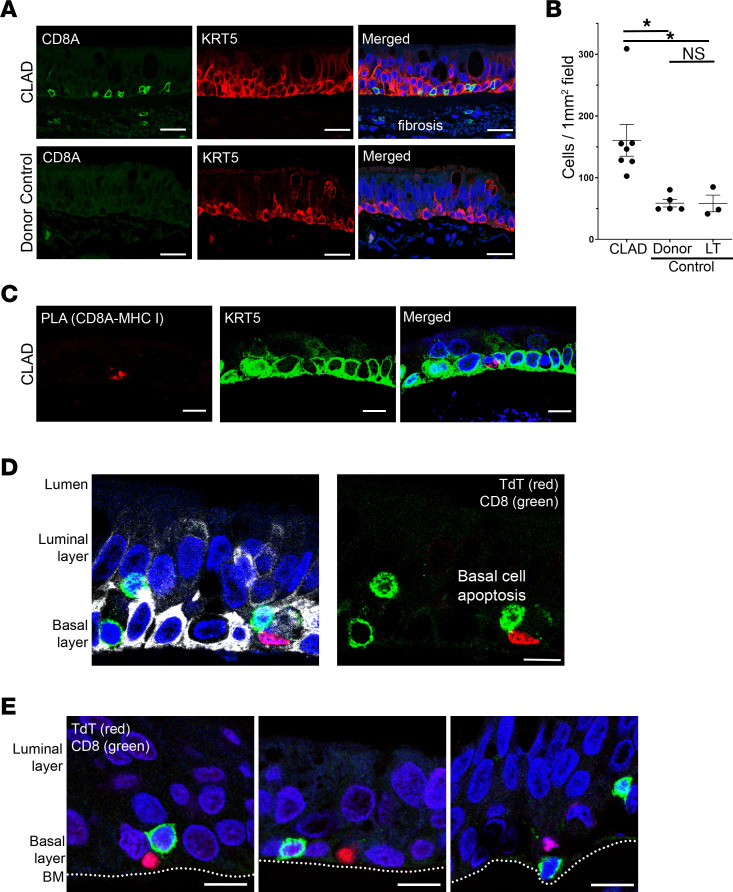
Figure 5. CD8+ T cells colocalize with KRT5+ basal cells and induce apoptosis in CLAD airways.
(A) Immunofluorescence staining for CD8+ T cells (CD8A, green) shows increased colocalization with basal cells (KRT5, red) in CLAD airways (top) compared with control airways (bottom) (n = 7 CLAD cases and 8 controls). Extensive fibrosis was notable in CLAD airways as indicated by nonspecific staining. Scale bar: 20 μm. (B) Quantification of immunofluorescence showing significantly increased CD8+ cells in CLAD airways compared with donor and lung transplant (LT) control tissue. There was no significant difference in CD8+ cell airway localization between the 2 control groups. (C) Proximity ligation assay with probes targeting CD8A and B2M (as a surrogate for MHC-I) identified a putative ligand-receptor interaction between CD8+ T cells and basal cells (KRT5) in CLAD airways. (D and E) TUNEL staining (TdT, red) revealed multiple cases of basal cell (KRT5, white) apoptosis in direct association with CD8+ T cells (CD8A, green) in CLAD airways that were not observed in control airways. Airway basement membrane (BM) is annotated for reference in E. Scale bar: 10 μm. Statistical analysis for immunofluorescence quantification (B) was performed using the 1-way ANOVA (P < 0.05) with post hoc Tukey test. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.