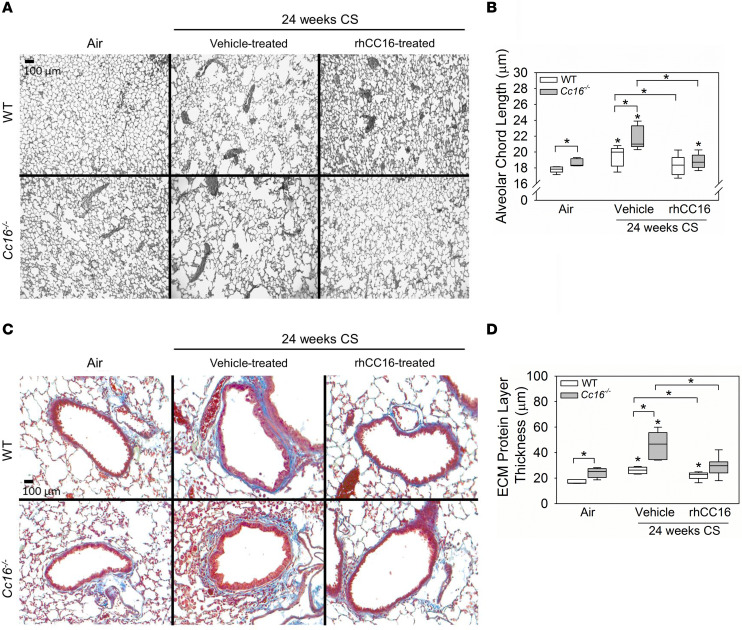
Figure 2. Treating WT and Cc16–/– mice exposed to CS for 24 weeks with rhCC16 limits the progression of COPD-like disease.
WT and Cc16–/– mice were exposed to air (5–6 mice/group) or CS for 24 weeks (12–13 mice/group), and rhCC16 (75 μg of rhCC16; 6–7 mice/group) or vehicle (6 mice/group) was delivered thrice weekly by the i.n. route to CS-exposed mice for the last 12 weeks of the CS exposures. Sections of inflated and fixed lungs were stained with either Gill’s stain (A) and alveolar chord lengths as a measure of airspace size were quantified (B) or with Masson’s trichrome stain (C, which stains extracellular matrix [ECM] proteins blue) and the thickness of the layer of ECM deposited around the small airways was quantified (D). In B and D, boxes in the box plots show the medians and 25th and 75th percentiles, and whiskers show the 10th and 90th percentiles. Data were analyzed using 1-way ANOVAs followed by pairwise testing with Mann-Whitney U tests. Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 vs. air-exposed mice belonging to the same genotype or the group indicated.