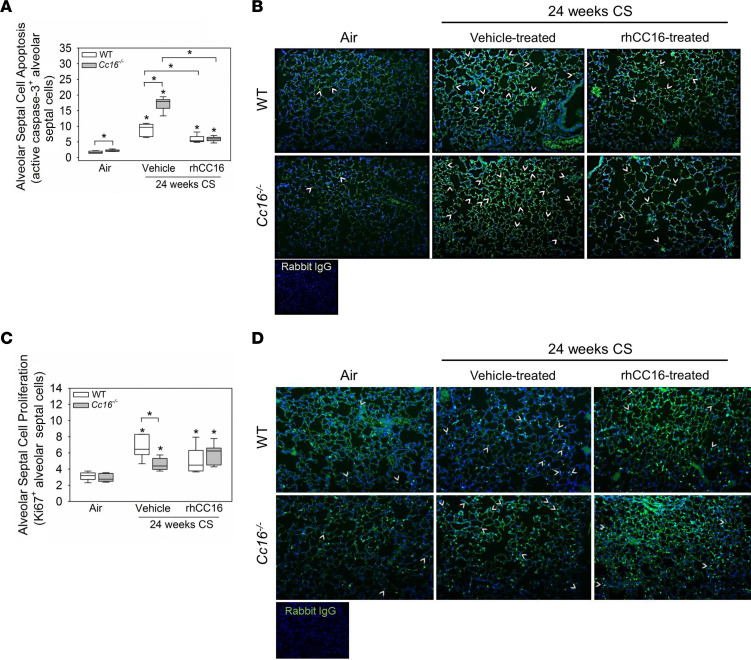
Figure 9. Treating CS-exposed WT and Cc16–/– mice with rhCC16 reduces alveolar septal cell apoptosis but not proliferation in their lungs.
WT and Cc16–/– mice were exposed to air (6–7 mice/group) or CS for 24 weeks (12–13 mice/group), and CS-exposed mice were treated with rhCC16 (75 μg of rhCC16; 6–7 mice/group) or vehicle (6 mice/group) for thrice weekly the last 12 weeks of the exposures. Inflated lung sections were immunostained for markers of alveolar septal cell apoptosis (active caspase-3; A and B) or proliferation (Ki67; C and D). Arrows point to active caspase-3–positive cells (B) or Ki67-positive cells (D). Boxes in the box plots show the medians and 25th and 75th percentiles, and whiskers show the 10th and 90th percentiles. Data were analyzed using 1-way ANOVAs followed by pairwise testing with Mann-Whitney U tests. Asterisks indicate P < 0.05 vs. air-exposed mice belonging to the same genotype or the group indicated.