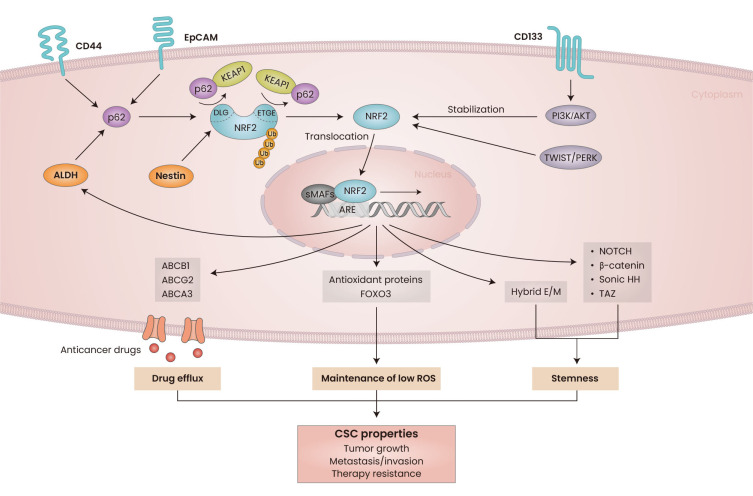
Fig. 3. Association of NRF2 with cancer stem cells (CSCs) properties.
NRF2 signaling is activated in CSCs and contributes to CSC properties, such as tumor initiation, metastatic malignancy, and therapy resistance. NRF2 is activated by CSC markers such as CD44, EpCAM, and ALDH, and p62 accumulation is associated with NRF2 activation. CD133 leads to NRF2 stabilization through PI3K/AKT pathway activation. TWIST-mediated PERK activation directly induce NRF2 accumulation. Competitive binding of Nestin with KEAP1 induces NRF2 liberation and translocation into the nucleus. NRF2 upregulates multiple antioxidant defense genes and FOXO3 to maintain low ROS levels. ABC transporters, including ABCB1, ABCG2, and ABCA3, are upregulated by NRF2 and contribute to chemotherapy resistance. High level of NRF2 is also associated with the upregulation of transcription factors, including NOTCH1/3, Sonic Hedgehog, β-catenin, and TAZ to maintain stemness of cancer cells. NRF2 activation stabilizes cells in hybrid epithelial/mesenchymal (hybrid E/M) state to support phenotypic conversion to CSCs. ROS, reactive oxygen species; EpCAM, epithelial cell adhesion molecule; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinases; sMAFs, samll MAF proteins; ARE, antioxidant response element; KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; DLG, DLG motif; ETGE, ETGE motif; ALDH, aldehyde dehydrogenase; NOTCH, neurogenic locus notch homolog protein; HH, hedgehog homolog.