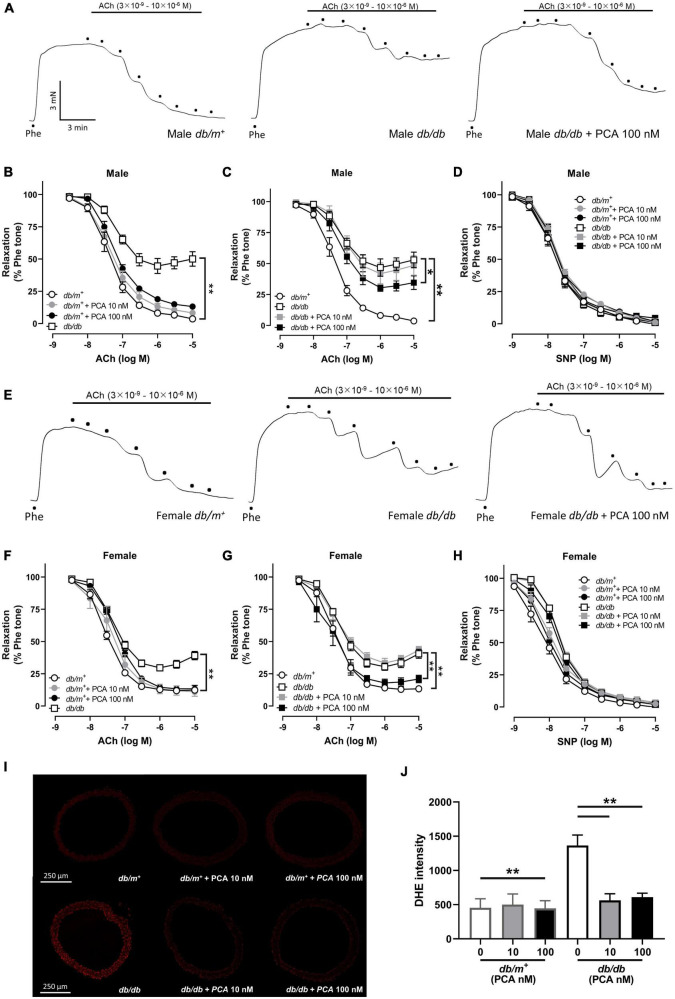
FIGURE 1.
Direct PCA incubation improved the endothelium-dependent relaxation (EDR) impairment in both male and female db/db mouse aortas with ROS suppression. Representative tracings (A) with summarized data (B,C) of EDR and endothelium-independent relaxation (D) measured by wire myograph in aortas from male db/m+ and db/db mice incubated with and without PCA (10 – 100 nM). Representative tracings (E) with summarized data (F,G) of EDR and endothelium-independent relaxation (H) measured by wire myograph in aortas from female db/m+ and db/db mice incubated with and without PCA (10 – 100 nM). Representative confocal images (I) and summarized data (J) of DHE stain intensity in aortic rings from db/m+ and db/db mice with and without PCA incubation (10–100 nM). Data are presented in means ± SEM; n = 5; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. PCA, protocatechuic acid; Phe, phenylephrine; ACh, acetylcholine; SNP, sodium nitroprusside; DHE, dihydroethidium.