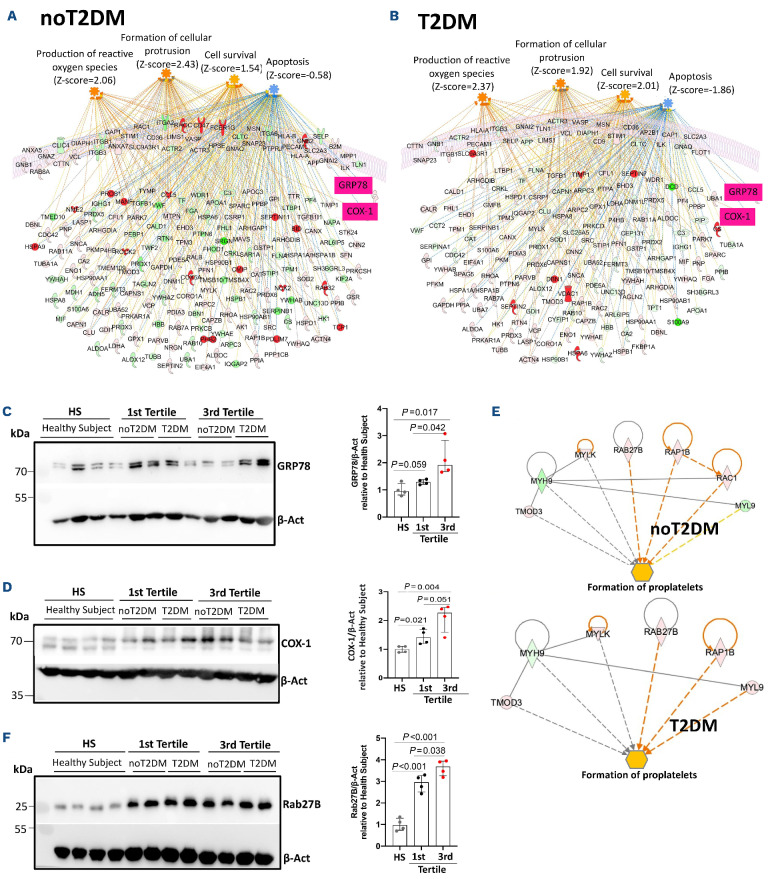
Figure 2.
Proteomic analysis shows activation of pathways “formation of cellular protrusions”, “formation of proplatelets”, “cell survival”, “production of reactive oxygen species”, and inhibition of “apoptosis” in platelets from patients with faster COX-1 recovery. Proteomic analysis using ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) revealed activation of “formation of cellular protrusions”, “formation of proplatelets”, “cell survival”, “production of reactive oxygen species”, and inhibition of “apoptosis” pathways in platelets of third vs. first serum thromboxane B2 (sTXB2) tertile in patients without (A, E), and with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) (B, E). Further details are reported in the Online Supplementary Figures S1, S2 and S3. Validation of proteomic data by western blot, assessing 78 kDa glucose-regulated protein (GRP78) (C) (n=4/tertile), COX-1 (D) (n=4/tertile) and Rab27B (F) (n=4/tertile) in patients from third tertile vs. first tertile and healthy subjects (HS) (n=4), using b-Actin as loading control. Significance was calculated by Student’s t-test.