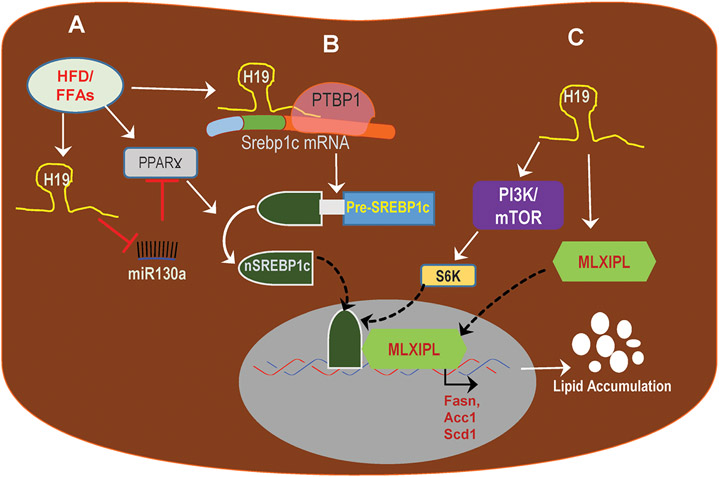
Fig.2. Potential mechanisms of H19-induced hepatic lipid accumulation.
HFD/FFAs induce upregulation of H19 in hepatocytes. A) H19 inhibits miR130a expression, an inhibitor of PPARƔ, and results in activation of PPARƔ and hepatic lipogenesis. B) H19 facilitates RBP, PTBP1, to stabilize the Srebp1c mRNA and promotes SREBP1c protein cleavage and nuclear translocation of the activated nuclear form, nSREBP1c and results in the increase of transcription of lipogenic genes. C) H19 induces activation of PI3K/mTOR pathway and upregulates lipogenic transcription factor, MLXIPL, resulting in increased lipid accumulation. HFD: High-fat diet; FFAs: free fatty acids; PPARƔ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor Ɣ; RBP: RNA binding protein; PTBP1: Polypyrimidine Tract Binding Protein 1; Srebp1c: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c; Mlxipl: MLX interacting protein-like; nSREBP1, the nuclear form of SREBP1c; PI3K/mTOR: phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin.