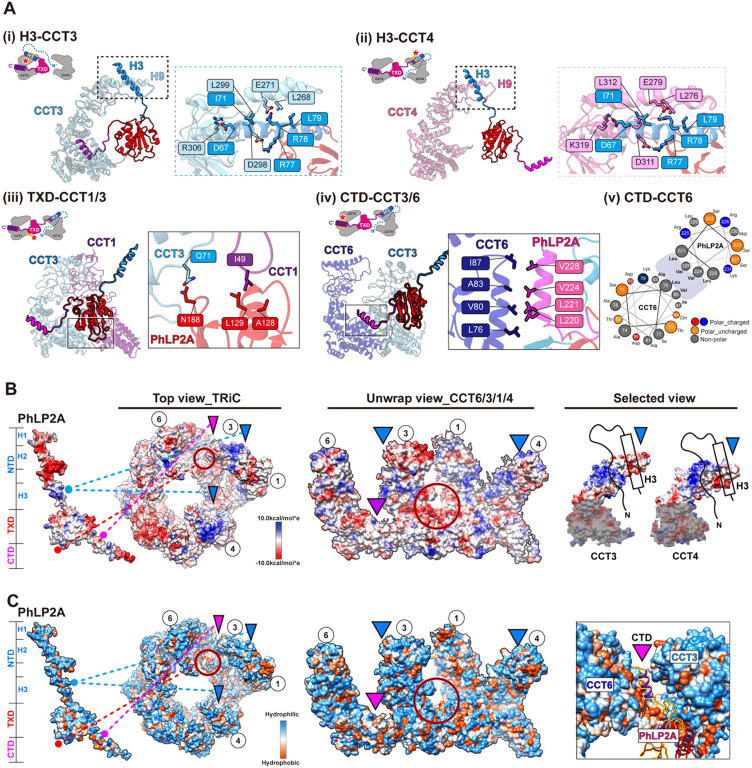
Figure 2. Molecular contacts between PhLP2A and open TRiC chamber.
(A) Detailed interaction between PhLP2A and TRiC. (i-ii) Zoomed-in view of the binding between PhLP2A H3 and the apical domain of CCT3 or CCT4. H9 and H10 of each CCT subunit are major interaction sites; their binding modes are similar either on the topological or sequence level. (iii) Inte raction between the lower part of TXD and the nucleotide-sensing loop of CCT1. (iv) Helix-to-helix i nteraction between PhLP2A CTD and CCT6. (v) Helix wheel diagram on PhLP2A CTD-CCT6 showin g the amphipathic nature of the helix. (B) Electrostatic surface charge of PhLP2A and open TRiC c hamber. PhLP2A, the top view of TRiC, and unwrap view of the CCT4/1/3/6 half-hemisphere are dis played. Binding sites between PhLP2A and TRiC are indicated with color-coded lines and triangles (dodger blue for the NTD and dark magenta for CTD of PhLP2A). The red circle indicates the TXD binding site to TRiC. Selected views focus on the part of the apical domain where H3 of PhLP2A bi nds via electrostatic charge interaction. (C) Surface hydrophobicity of PhLP2A and the open TRiC ch amber. Interactions between PhLP2A and TRiC are indicated in (B). While other binding sites are m ainly hydrophilic, the TXD binding interface between CCT1/3 and the CTD binding crevasse between CCT3 and 6 are hydrophobic.