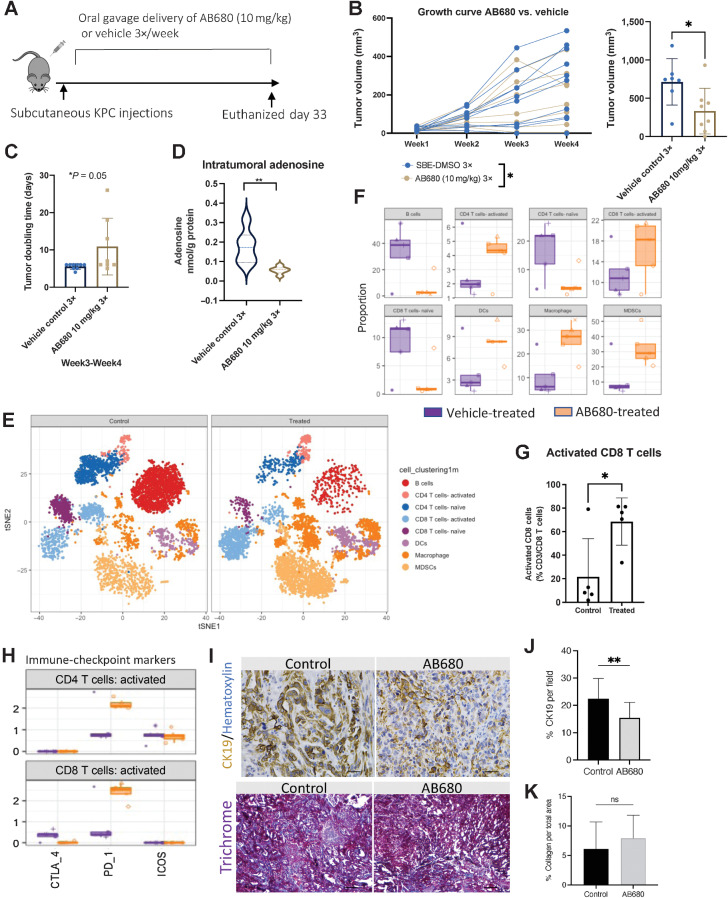
Figure 5.
AB680 oral gavage treatment reduces tumor KPC tumor growth rate and elevates intratumoral activated CD8+ T cells. A, KPC subcutaneous tumors were analyzed weekly (n = 10 per group). B, AB680 treatment significantly decreased KPC subcutaneous growth rates and at the conclusion of this experiment, AB680-treated mice had significantly smaller tumor volume than vehicle control-treated mice. *, P < 0.05. Statistical analysis was performed using a Student t test in Prism GraphPad software. C, Graphical representation of subcutaneous tumor growth rates for analysis of individual tumor doubling time. n = 6. *, P < 0.05. D, HPLC analysis shows a significant decrease in adenosine levels in tumors from AB680-treated mice versus vehicle-treated mice. **, P < 0.01 compared with vehicle controls (n = 8 per group). E, CyTOF vSNE plots by group show elevated clusters of activated CD8 T cells, CD4 T cells, MDSCs, and macrophages. F, Quantitative global population analysis reveals increased activated CD4 T cells, CD8 T cells, macrophages, and MDSCs. G, Quantitative analysis of significantly increased activated CD8 T cells. *, P < 0.05. A Student test using Prism GraphPad software was used to calculate statistics. H, Activated CD4 and CD8 T cells increased expression of PD-1. I, Representative CK19 and trichrome staining of tumors from control- (vehicle) and AB680-treated mice. J and K, Tumors from AB680-treated mice had significantly reduced expression of CK19 (**, P < 0.01; J) and no significant difference (ns) in % collagen per total area (K). Scale bars, 50 μm.