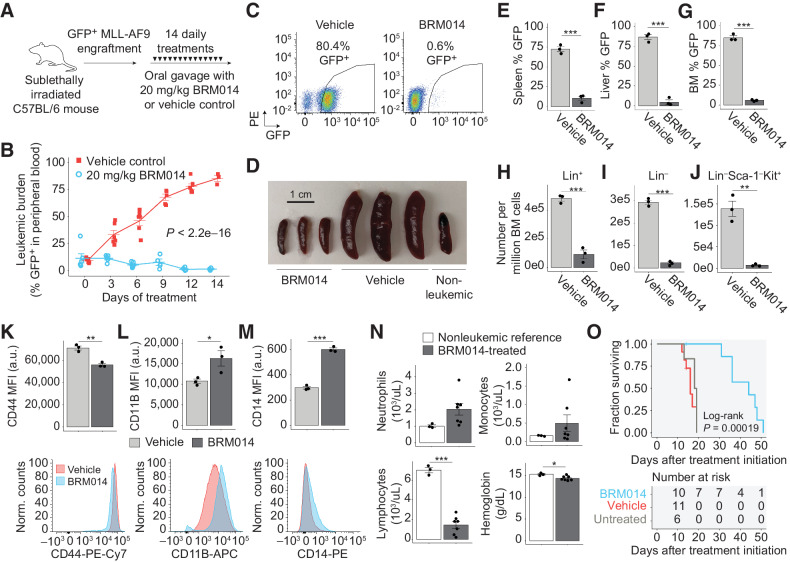
Figure 5.
SWI/SNF inhibition has a significant therapeutic window against AML in an immunocompetent setting. A, Dosing scheme for in vivo treatment of MLL-AF9 leukemia with BRM014 or vehicle control. B and C, Leukemic burden of mice treated with BRM014 or vehicle control over the two-week treatment period (B) and quantification by flow cytometry (C). N = 11, vehicle; N = 10, BRM014. D, Spleens harvested after 14 days of treatment with BRM014 or vehicle control. E–G, Leukemic burden in the spleen (E), liver (F), and BM (G) of mice treated with BRM014 or vehicle control. N = 3 per condition. H–J, Effect of BRM014 on the number of committed (Lin+; H), uncommitted (Lin–; I), and LSC-enriched Lin–Sca-1−Kit+ stem/progenitor cells (J) within the leukemic population in BM. Cells in H, I, and J were gated on the basis of GFP+ cells. N = 3 per condition. K–M, Expression of stemness (CD44; K) and myeloid differentiation markers CD11B (L) and CD14 (M) on leukemic GFP+ cells in the BM of mice treated with BRM014 or vehicle control. N = 3 per condition. N, CBC neutrophil, monocyte, and lymphocyte counts and hemoglobin levels in BRM014-treated mice versus nonleukemic controls 3 days after completion of treatment course. N = 3, nonleukemic; N = 7, BRM014. O, Survival of MLL-AF9 mice treated with BRM014 or vehicle control. N = 6, untreated; N = 11, vehicle; N = 10, BRM014. Error bars, mean ± SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.