Figure 6.
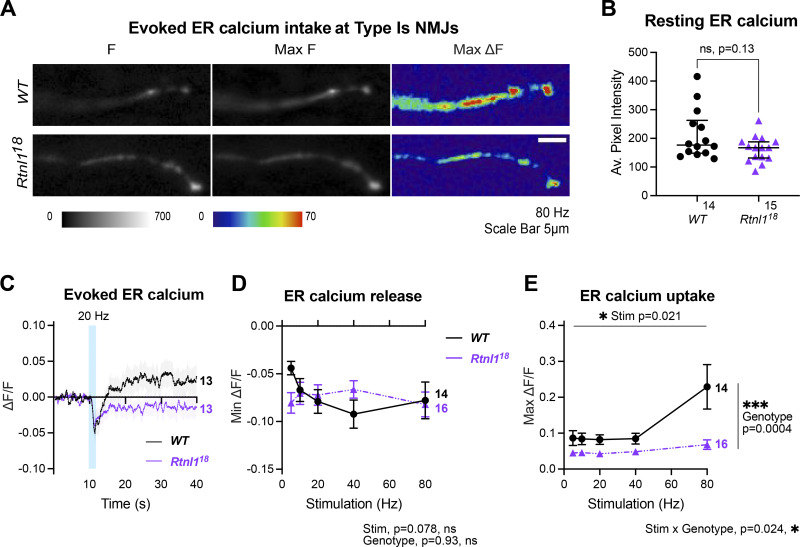
Rtnl1 loss decreases evoked ER Ca2+ uptake at Type Is termini. Evoked ER Ca2+ responses were measured at Type Is termini at muscle 1 in segment A4-A6. (A) Lumenal GCaMP fluorescence at Type Is NMJs, presented at rest (F), maximum fluorescence (Max F), and maximum change in fluorescence (Max ΔF) in representative examples of WT and Rtnl118 presynaptic terminals. (B) Loss of Rtnl1 does not affect resting ER Ca2+. The graph shows larval datapoints as in Fig. 5 B, with median ± interquartile ranges, compared using a Mann–Whitney U-test. (C) ΔF/F timecourse of evoked lumenal GCaMP responses to 20 Hz stimulation (mean ± SEM). (D) Loss of Rtnl1 does not affect ER Ca2+ release immediately following stimulation. The graph shows the minimum ΔF/F value after stimulation. (E) Loss of Rtnl1 significantly decreases evoked ER Ca2+ uptake over a range of stimulation frequencies. The graph shows the maximum ΔF/F value reached after stimulation. In D and E, graphs and analyses are as for Fig. 5 D. Genotypes: Is-GAL4, UAS-ER-GCaMP6-210/UAS-tdTom::Sec61β in either a WT or Rtnl118 mutant background.