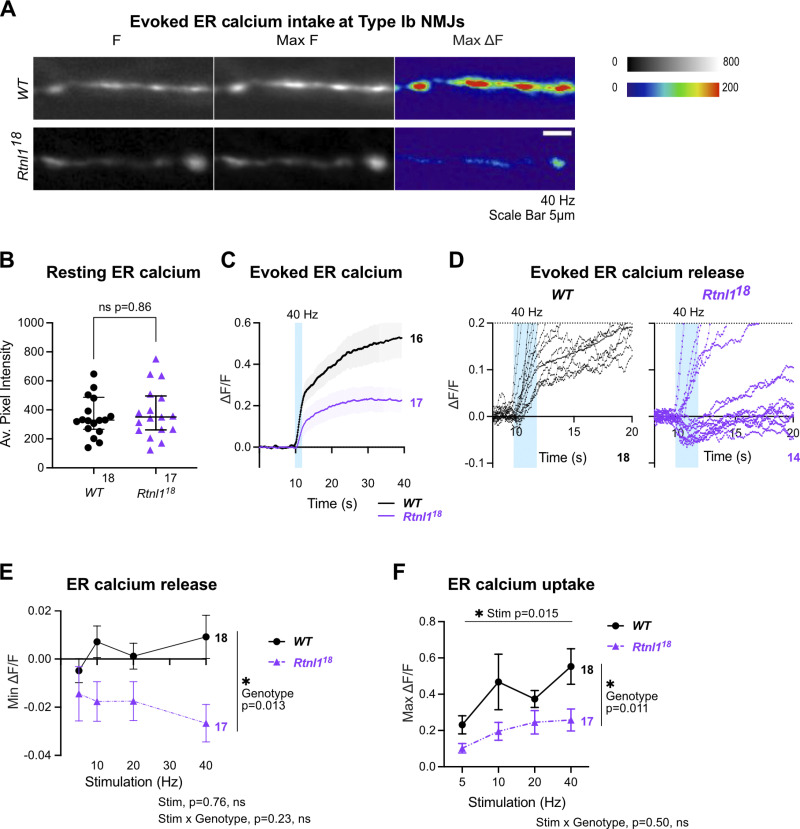
Figure 7.
Rtnl1 loss decreases evoked ER Ca2+ uptake in Type Ib termini. Evoked ER Ca2+ responses were measured at Type Ib termini at muscle 1 in segment A4-A6. (A) Lumenal GCaMP fluorescence at Type Ib NMJs presented as in Fig. 6 A. (B) Loss of Rtnl1 does not affect resting ER resting lumen GCaMP. Graphing and analysis are as for Fig. 6 B. Some outlier datapoints are excluded from the graph but included in statistics. (C) ΔF/F time course of evoked lumenal GCaMP responses to 40 Hz stimulation (mean ± SEM). (D) ΔF/F time courses from individual larvae show that transient evoked Ca2+ release from ER, common in Type Is termini (Fig. 6 C) is mostly undetectable in WT Type Ib termini but found in over half of Rtnl118 Type Ib termini tested. (E) Loss of Rtnl1 increases ER Ca2+ release across a range of stimulation frequencies. (F) Loss of Rtnl1 significantly decreases evoked ER Ca2+ uptake over a range of stimulation frequencies. Graphs in E and F are presented and analyzed as in Fig. 5 D. Genotypes: Ib-GAL4, UAS-ER-GCaMP6-210/UAS-tdTom::Sec61β in either a WT or Rtnl118 mutant background.