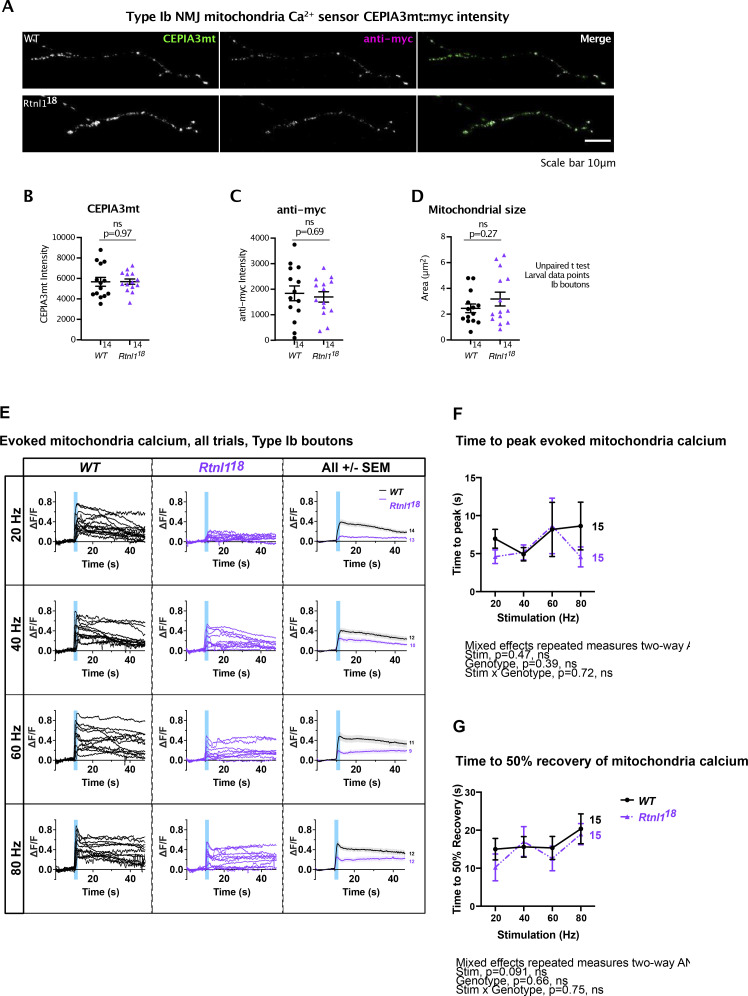
Figure S13.
Effect of Rtnl1 loss on mitochondrial Ca2+ handling in Type Ib boutons. (Extended data from Fig. 8.) (A) Panels show mitochondrial CEPIA3mt fluorescence and anti-myc signal of CEPIA3mt::myc in typical examples of WT and Rtnl118 muscle 1, Type Ib postsynaptic terminals. (B–D) Rtnl1 loss-of-function does not impact CEPIA3mt fluorescence intensity (B), anti-myc signal intensity (C) of CEPIA3mt::myc, or mitochondrial size (D). Plots shows individual larval datapoints and mean ± SEM; sample size (larvae) is indicated within the plot for each genotype. For each larva, all mitochondria from several muscle 1 NMJs between A2-A6 segments were analyzed, and each mean larval value is shown as a datapoint. Pairwise comparisons were performed using Student’s t tests. Genotypes are Ib-GAL4, CEPIA3mt::myc, in either a WT or Rtnl118 background. (E) Impact of Rtnl1 loss-of-function on peak evoked mitochondria Ca2+. Plots show all single time traces and mean ± SEM time traces in both genotypes for the four stimulation frequencies tested. Sample size (larvae) is indicated within the plot for each genotype. (F and G) Rtnl1 loss of function does not affect time to peak mitochondria Ca2+ or (G) time to 50% recovery of mitochondria Ca2+. Plots show mean ± SEM of every genotype for each stimulation frequency tested; sample size (larvae) is indicated within the plot for each genotype. For each larva, responses from a 50-s recording from one muscle 1 NMJ between A4-A6 segments were analyzed. Datapoints represent the time between stimulation and peak ΔF/F or peak ΔF/F and half recovery. Comparisons were analyzed with a mixed-effects two-way ANOVA. Genotypes are Ib-GAL4, UAS-CEPIA3mt::myc/UAS-tdTom::Sec61β, in either a WT or Rtnl118 background.