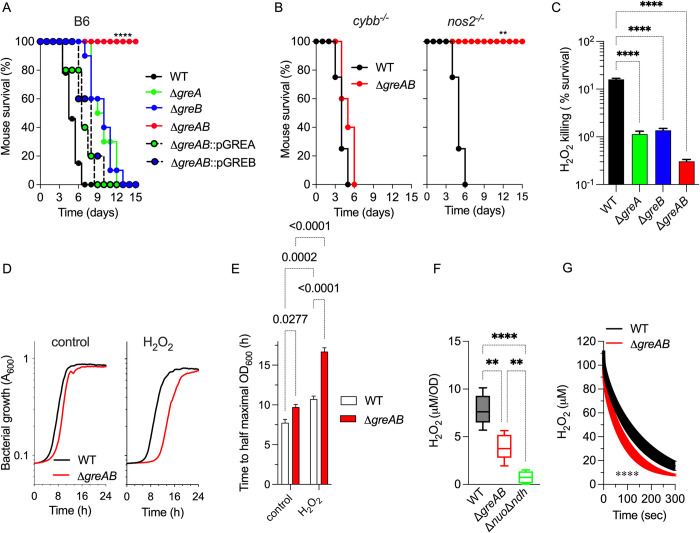
Fig 1. Gre factors regulate resistance of Salmonella to the antimicrobial activity of NOX2.
Survival of C57BL/6 (A), cybb-/- and nos2-/- (B) mice after i.p. inoculation of 100 CFU of the indicated strains of Salmonella (N = 10). Statistical differences (p < 0.0001) were calculated by logrank analysis. The ΔgreAB mutant was complemented with either greA or greB genes expressed from their native promoters in the low copy number pWSK29 plasmid (i.e., pGREA and pGREB, respectively). (C) Killing of Salmonella 2 h after treatment with 400 μM H2O2. Bacterial cultures were grown overnight in LB broth, diluted to 2 × 105 CFU/ml in PBS and treated for 2 h with 400 μM H2O2. Killing, expressed as percent survival compared to the bacterial burden at time zero, is the mean ± SD (N = 12–16); p < 0.0001 as determined by one-way ANOVA. (D) Growth of wild-type (WT) and ΔgreAB mutant Salmonella in EG minimal medium (pH 7.0), at 37°C in the presence or absence of 200 μM H2O2 as measured by OD600 in a Bioscreen plate reader. Data are shown as the mean (N = 11–12). (E) Time to reach half maximal OD600 was calculated from curves in panel D. Data are the mean ± SD. p determined by two-way ANOVA. Endogenous H2O2 synthesis (F) and H2O2 consumption (G) by log phase Salmonella grown in MOPS-GLC medium (pH 7.2), at 37°C with shaking to an OD600 of 0.25. H2O2 was measured polarographycally in an APOLLO 4000 free radical analyzer. (G) Cultures were treated with 100 μM H2O2 at the time of measurement. Data are the mean ± SD. (N = 5 in E; N = 6 in F). **, **** p < 0.01 and p < 0.0001 as determined by one-way ANOVA (F) or t test (G). LB, Luria–Bertani; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; WT, wild-type.