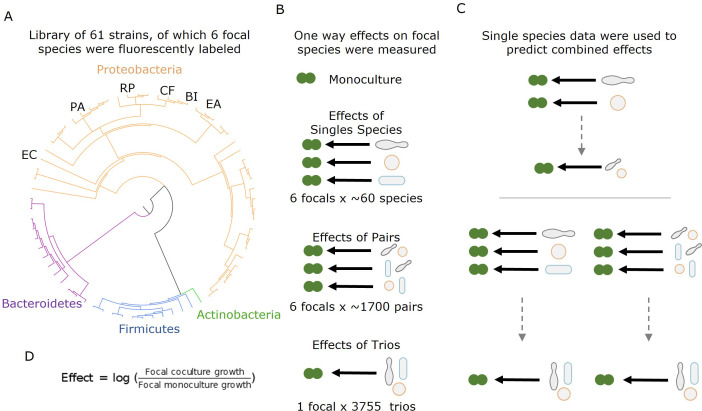
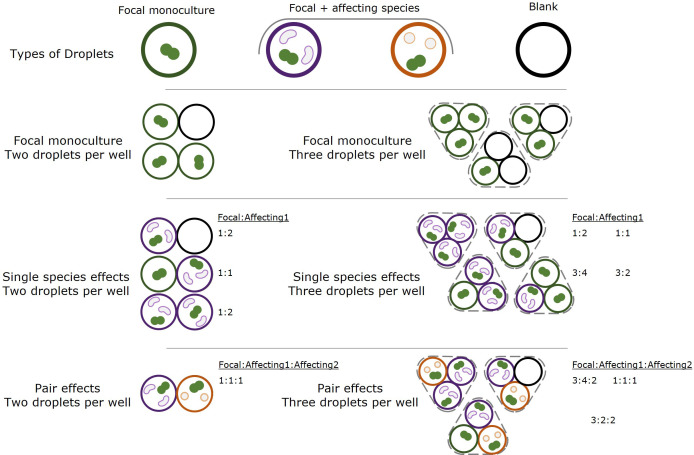
Figure 1. Measuring effects of 61 affecting species, and their pairs and trios on 6 focal species.
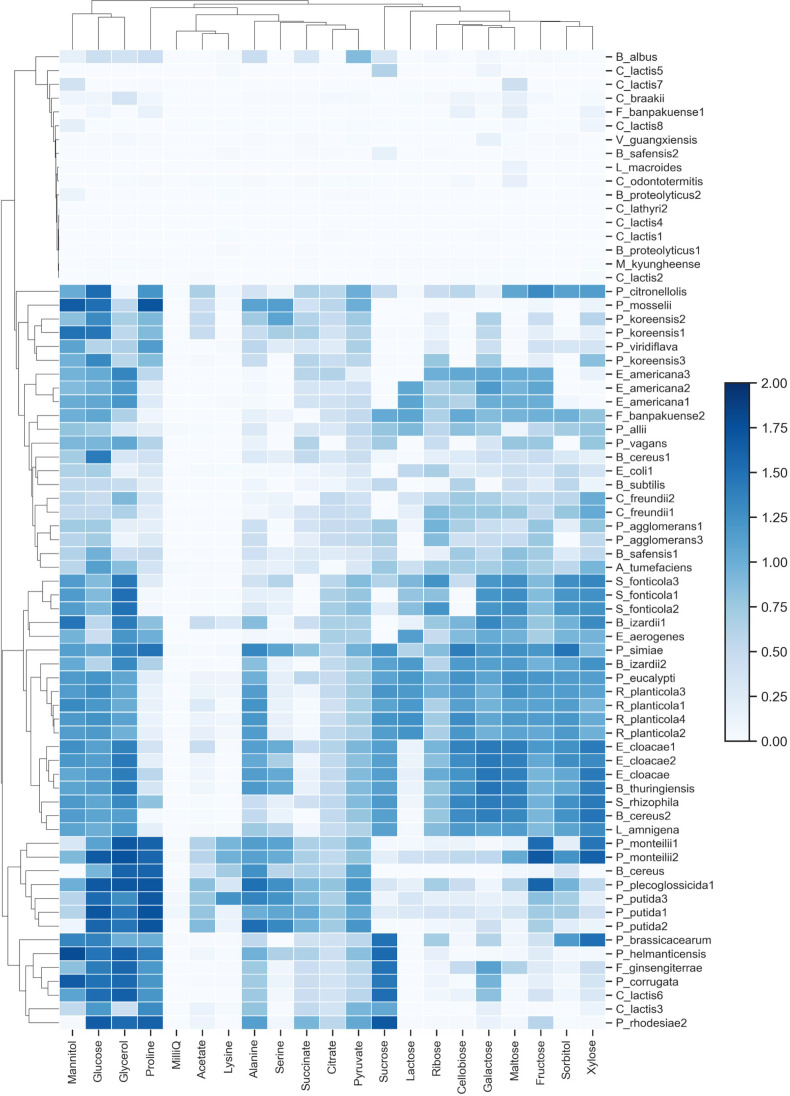
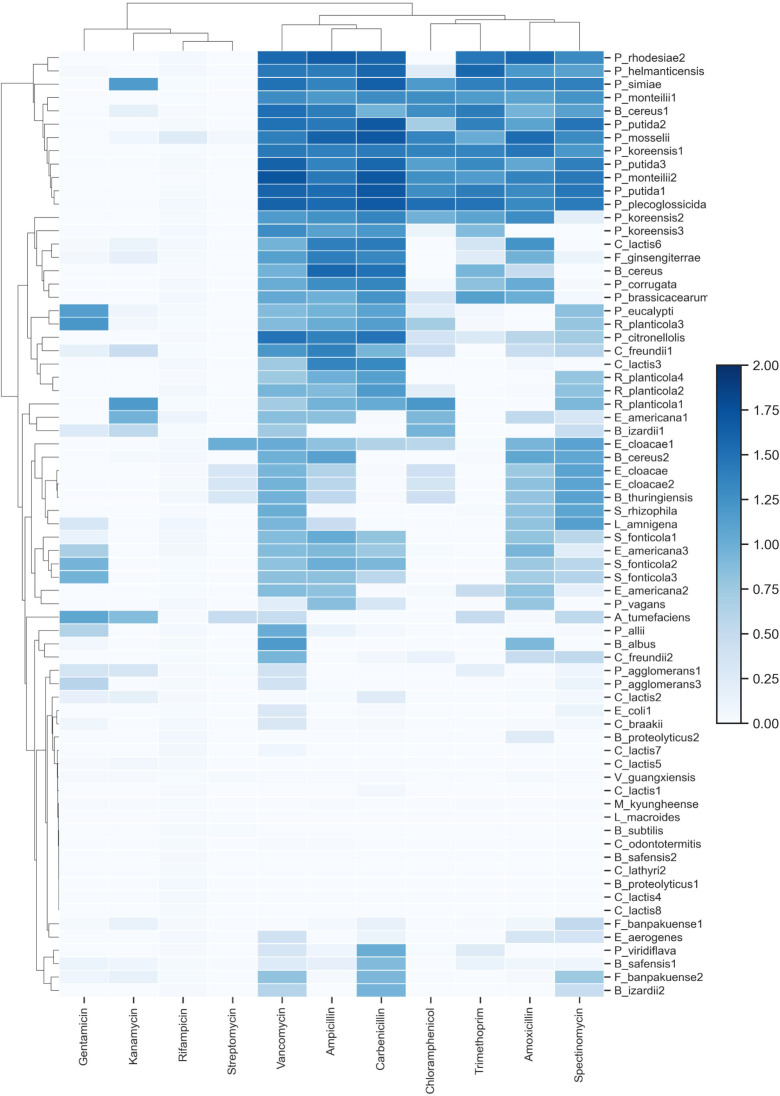
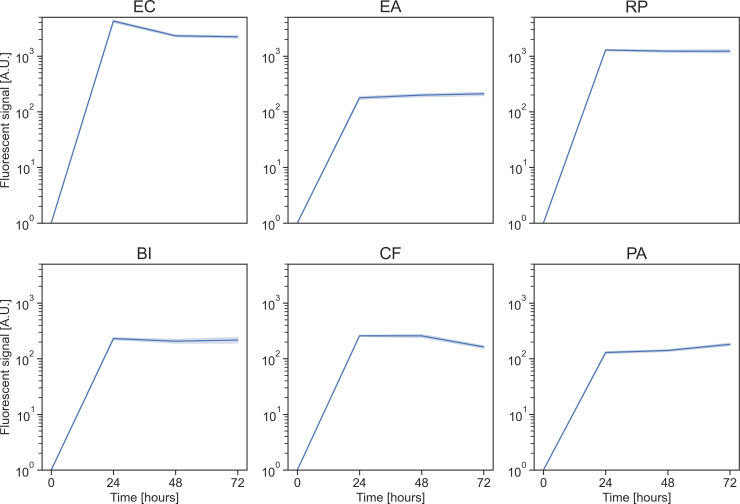
(A) A library of 61 soil and leaf-associated bacterial strains was used in this experiment. All strains are from four orders: Proteobacteria (orange), Firmicutes (blue), Bacteroidetes (purple), and Actinobacteria (green) (full list in Supplementary file 1a, Source data 1). Also, 6 of the 61 species were labeled with GFP and used as ‘focal’ species whose growth was tested in the presence of the other isolates (affecting species). These strains are labeled on the phylogenetic tree (Escherichia coli [EC], Ewingella americana [EA], Raoultella planticola [RP], Buttiauxella izardii [BI], Citrobacter freundii [CF], and Pantoea agglomerans [PA].) (B) Each focal species was grown in monoculture, with (between 18 and 52) single affecting species, and (between 153 and 1464) pairs of affecting species. Additionally, E. coli was grown with 3009 trios of affecting species. (C) Effects of pairs and trios were then predicted using the effects of single species and single species and pairs, respectively. Predictions were made using three different models: additive, mean, and strongest (detailed in ‘Results’ and ‘Materials and methods’). (D) Equation used for calculating the effect of an affecting species on the focal species.