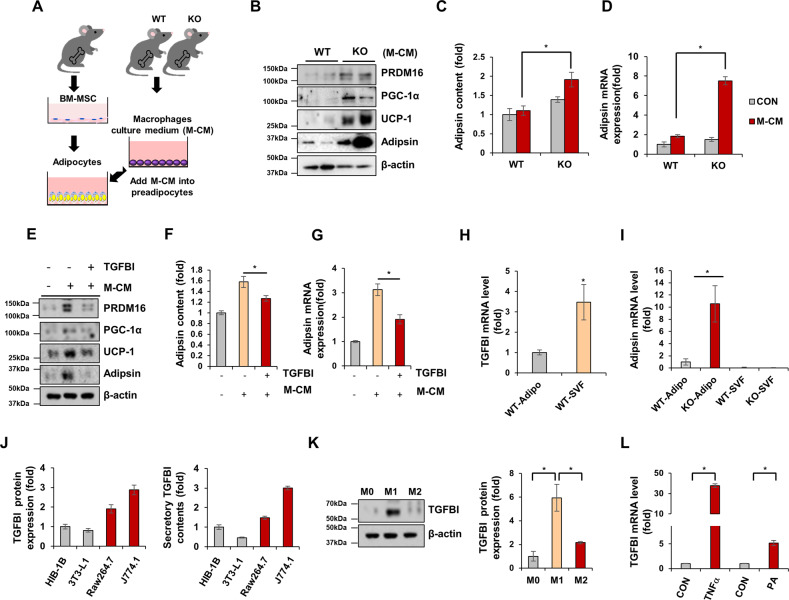
Fig. 4. TGFBI-deficient macrophages induced increased adipsin and browning-related protein expression on adipocytes in a paracrine manner.
A Schematic of the experimental design. BM-MSCs were isolated from WT mice and induced to differentiate with M-CM obtained from WT or KO mice. B Expression of the indicated proteins in differentiated BM-MSCs cultured with WT or KO macrophages. C-D Secretory and mRNA expression of adipsin in the above cells. E-G BM-MSCs were either unstimulated or treated with 10 µg recombinant TGFBI under coculture conditions with TGFBI KO macrophages. Expression of the indicated proteins (E) and secretory (F) and mRNA (G) levels of adipsin in the above cells. H–I Adipocytes and SVFs were isolated from iWAT obtained from WT and KO mice. The mRNA expression of TGFBI (H) and adipsin (I) was measured in the indicated fractions. J TGFBI expression in differentiated HIB-1B and 3T3-L1 adipocytes and Raw264.7 and J774.1 macrophages (M1 phenotype) was assessed by western blot analysis (left) and ELISAs (right). K Human THP-1 macrophages were treated with 10 ng/mL LPS and 20 ng/mL IFN-γ or 20 ng/mL IL-4 and 20 ng/mL IL-13 for polarization into M1 and M2 macrophages, respectively. TGFBI expression was verified and quantified (right panel). L THP-1 macrophages were treated with rhTNFα (20 ng/mL) and palmitic acid (200 µM). TGFBI mRNA expression was verified. Error bars represent the ± SEM. *p < 0.05 by two-sided t test.