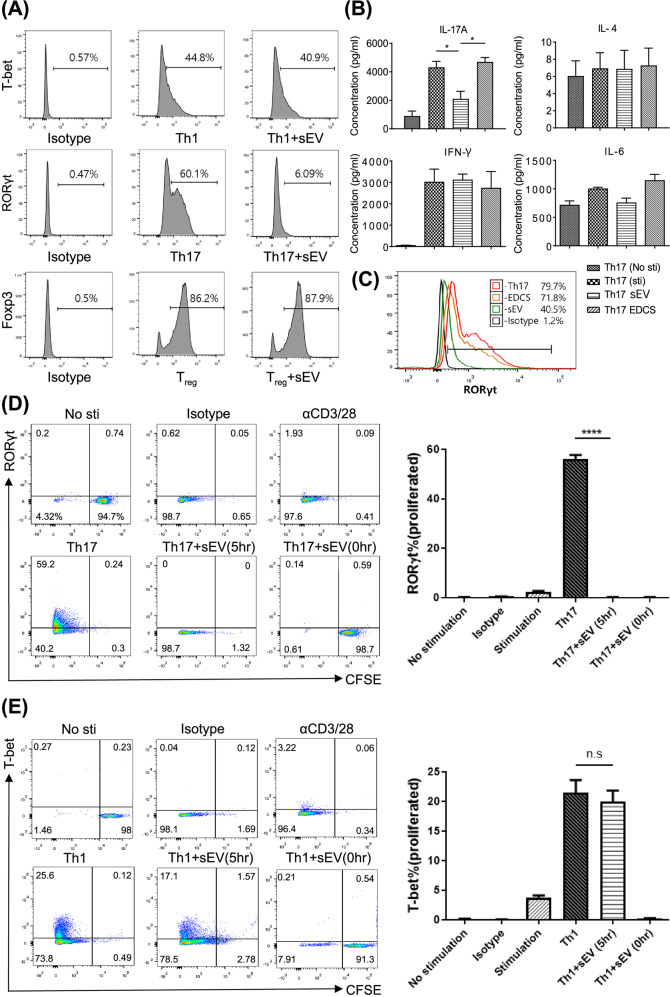
Fig. 2. MSC-sEVs specifically inhibited Th17 cells by targeting RORγt.
A Effect of MSC-sEVs on Th1, Th17, and Treg cell differentiation. Naïve CD4+ T cells differentiated into Th1, Th17, and Treg cells in the presence of MSC-sEVs. The expression of transcription factors (T-bet for Th1, RORγt for Th17, and Foxp3 for Treg) was analyzed by FACS. MSC-sEVs significantly reduced the number of RORγt+ T cells but not Foxp3+ and T-bet+ T cells. B Effect of MSC-sEVs on the cytokine secretion by Th17 cells. The levels of IL-17A, IL-4, IFN-γ, and IL-6 secreted from Th17 cells cocultured with MSC-sEVs were measured by the cytometric bead array (CBA) assay. Treatment with sEVs decreased the production of IL-17 but not other cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-4, and IL-6, by Th17 cells. C Analysis of RORγt expression levels after Th17 differentiation in the presence of MSC-sEVs. sEVs-depleted culture serum (EDCS) and sEVs were used to treat differentiated Th17 cells. EDCS failed to reduce the number of RORγt+ T cells, indicating that MSC-sEVs were key players in the suppression of Th17 differentiation. D, E Assessment of the proliferation level of Th1 and Th17 cells treated with MSC-sEVs. Naive CD4+ T cells were labeled with CFSE (5 µM, 5 min) and differentiated into Th1 and Th17 cells under MSC-sEVs treatment conditions. sEVs specifically suppressed the differentiation of Th17 cells, and their mechanisms were independent of cell cycle arrest. A representative image from the three independent assays is shown in the dot plot. The percentages of RORγt- and T-bet-positive cells among the proliferating cells are shown in the plot. The mean of triplicates is displayed as a bar graph, and the error bars indicate SEM. ****p ≤ 0.0001.