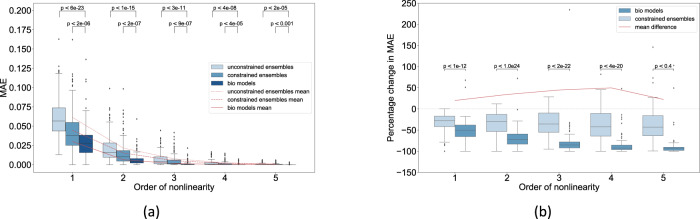
Fig. 2. Biological models are more approximable than expected by chance.
a The MAE of the biological models and the associated constrained and unconstrained ensembles for approximation orders 1 to 5; MAE values for orders 6 and above are negligible and not shown. b Percentage change in MAE for the biological models and the associated constrained ensembles computed with respect to the MAE of the corresponding unconstrained ensembles. Every point in the distributions corresponding to the random ensembles represents the average MAE of an ensemble of 100 random networks associated with each biological model. The p values indicate the statistical significance of the difference in mean MAEs between sets of random ensembles and the biological models for a given order of nonlinearity. Statistical analysis by Welch’s unequal variances t-test.