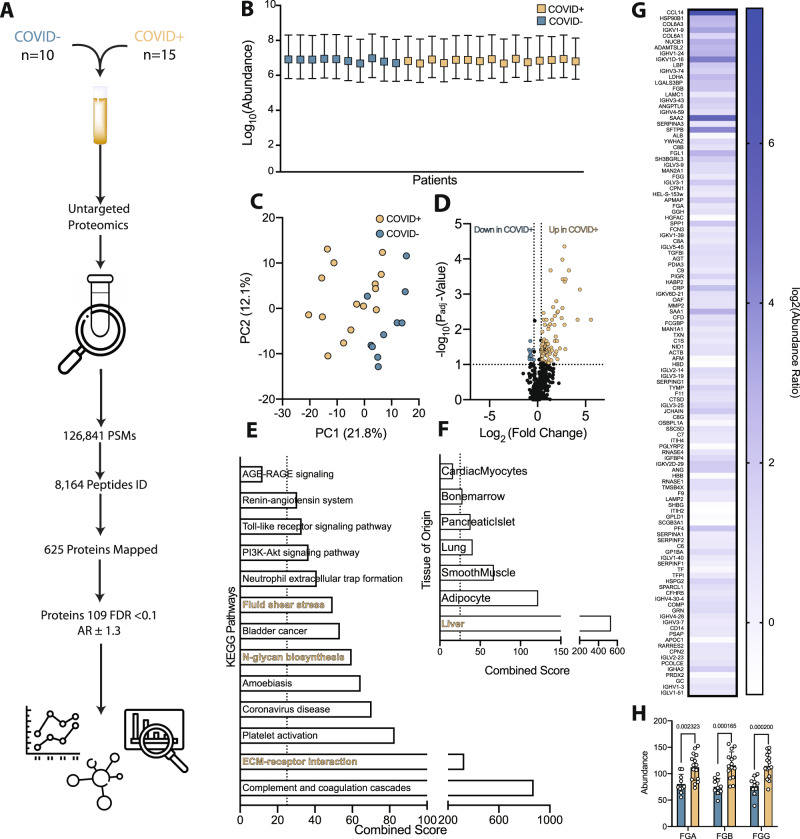
Fig. 1. Proteomics analysis comparing adult plasma from critically ill COVID + and COVID- patients uncovers significant alterations in liver-related proteins and hemodynamic-related pathways.
A Schematic overview of the approach and identified species in the adult cohorts of COVID + and COVID- critically ill patients. B Relative abundance of detected peptides per patient sample (COVID + n = 15, COVID- n = 10, SD). C Principal component analysis (PCA) plot of proteomics data demonstrating clustering and partial separation of plasma samples from COVID + and COVID- adults. D Volcano plot showing relative distribution of identified proteins (One-way ANOVA test, Benjamini-Hochberg correction). E KEGG pathway analysis of differentially abundant proteins (DAPs) highly upregulated (Padj > 0.1 AR > 1.4) in COVID + patients highlights alterations in fluid shear stress response pathways (gold) and previously reported changes in ECM receptor interactions (also gold), (Fishers exact test). F Comparison of DAPs to the human genome atlas showing relative origin of proteins identified highlights perturbations in liver, lung, and immune cell homeostasis. G Heat map of DAPs identified by proteomics analysis that are altered in COVID + adults as compared to COVID- adults. H The abundance of all 3 chains of the hepatic acute phase protein fibrinogen is increased in COVID + compared to COVID- adult patients (COVID + n = 15, COVID- n = 10, two-tailed t-test, SD). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.