Fig. 1. Biogenic Nanoparticles.
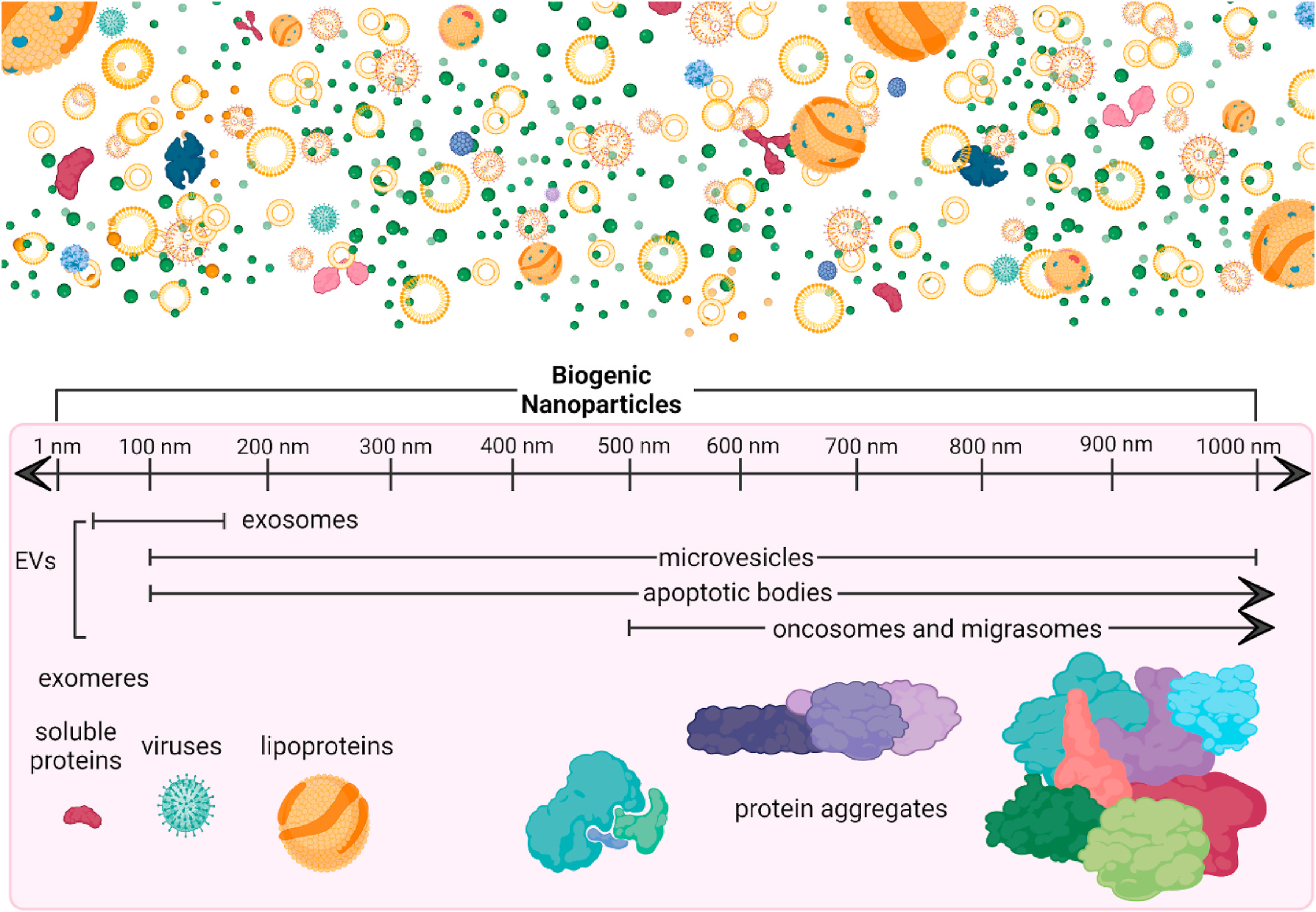
Biogenic nanoparticles include extracellular vesicles (EVs) and other nanosized extracellular particles. Newer inclusions are exomeres: non-membranous nanoparticles smaller than 50 nm, with functional contents secreted by cells (H. Zhang et al., 2018), oncosomes: EVs released from cancer cells ranging between 100 nm and 4 μm (Meehan et al., 2016), and migrasomes: large nano- and microvesicles used for cell migration and intercellular signaling (da Rocha-Azevedo and Schmid, 2015; Ma et al., 2015). More well-established nanoparticles include lipoproteins (Feingold, 2000), viruses (Louten, 2016), and protein aggregates (Goodsell and Olson, 1993). This figure was created in ©BioRender-biorender.com.
