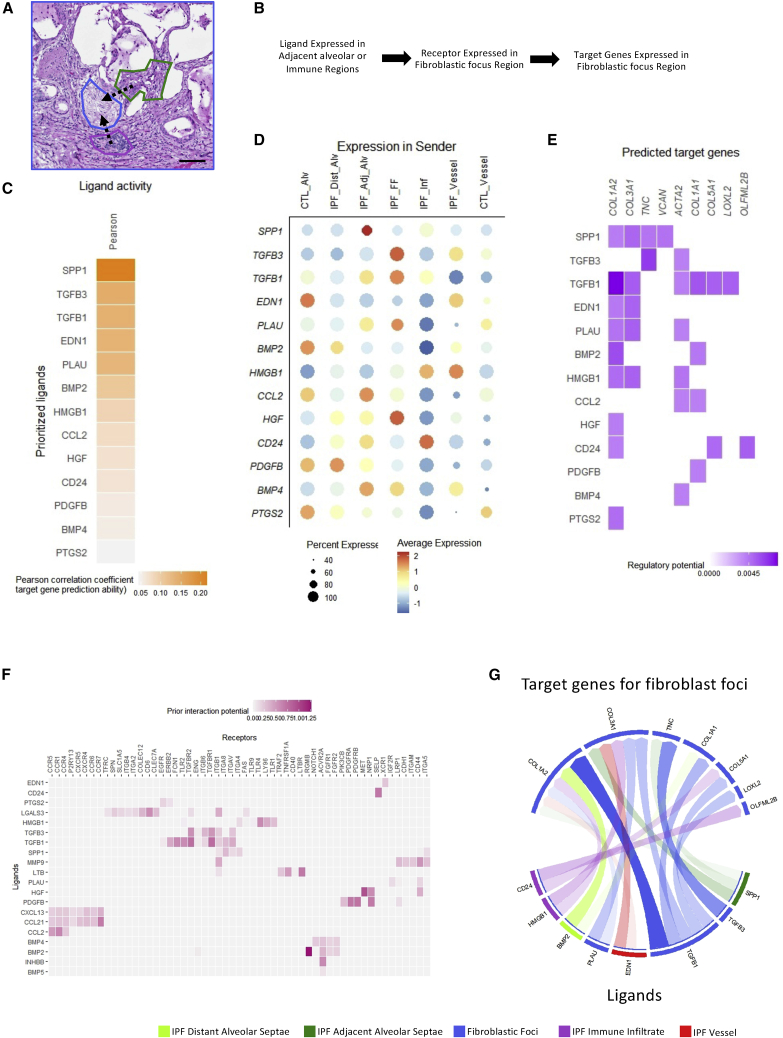
Figure 5.
Ligand-receptor interactions within the fibrotic niche
(A) Representative H&E stained IPF lung tissue section of a fibroblast focus, immune infiltrate, and adjacent alveolar septae within the fibrotic niche following digital spatial profiling. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(B) Schematic of NicheNet workflow. Nichenet predicts communications based on ligand expression in sender regions, receptor expression in receiver regions, and signaling within the sender regions.
(C) Pearson correlation coefficients of ligands and target genes in adjacent ROIs.
(D) Dot blot showing mean ligand expression in different ROIs.
(E) Regulatory potential of predicted target genes in IPF fibroblastic foci.
(F) Receptors expressed within fibrotic foci regions that can potentially bind to ligands found in (C). Heatmap shows the regulatory potential for ligand-receptor pairs based on prior interaction knowledge.
(G) Results from (C)–(E) summarized in a circus plot. Arrow transparency indicates regulatory potential between ligand and target gene. Arrows are colored depending on the region in which the ligand is most highly expressed.