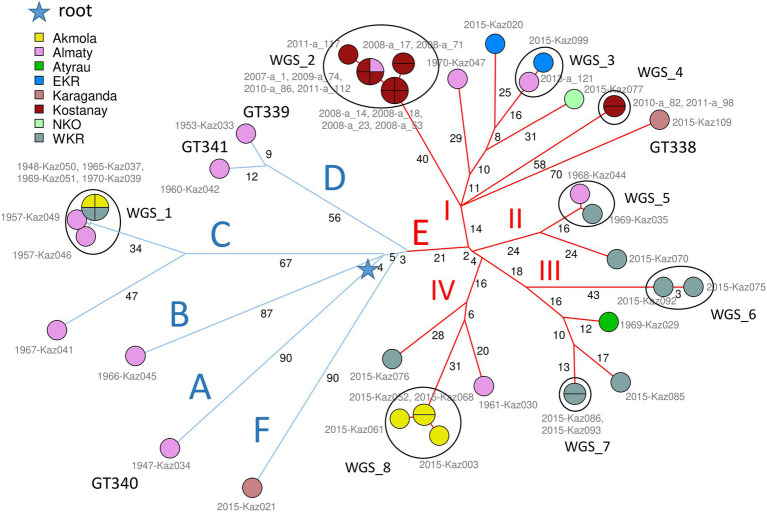
Figure 1.
Brucella abortus subclade C1, 46 strains from Kazakhstan. Maximum parsimony tree based on core genome SNPs. 1,146 SNPs were called by mapping on genome accession GCA_000740155 (B. abortus clade B strain Tulya). The size of the resulting tree is 1,151 SNPs (homoplasia 0.44%). Thirty-three whole-genome SNP (wgSNP) genotypes are resolved. Branch lengths of two SNPs and more are indicated by black numbers. Strains are labeled in gray with collection year and strain Ids and colored according to region of origin as indicated. The MLVA11 genotype is indicated for new lineages distinct from GT72 (GT338 to GT341). The blue star indicates the root of the phylogeny (branching point toward B. melitensis type strain 16 M used as outgroup). From the blue star, early splits define six branches, labeled A to F. Blue branches A to D are defined by a few ancient strains isolated between 1947 and 1970. Blue branch F is defined by one recent strain, KAZ021 isolated in 2015. Red branch E with 34 strains (24 wgSNP genotypes) is remarkable by its diversity (24 wgSNP genotypes) and high number of associated strains (34 out of 46). It contains all but one of the recent strains (isolated in 2007–2015) together with five ancient strains. The E branch is structured into four subbranches labeled I to IV in red. Strains closely related or coincident in terms of wgSNP genotype define eight clusters labeled WGS_1 to WGS_8.