Figure 4.
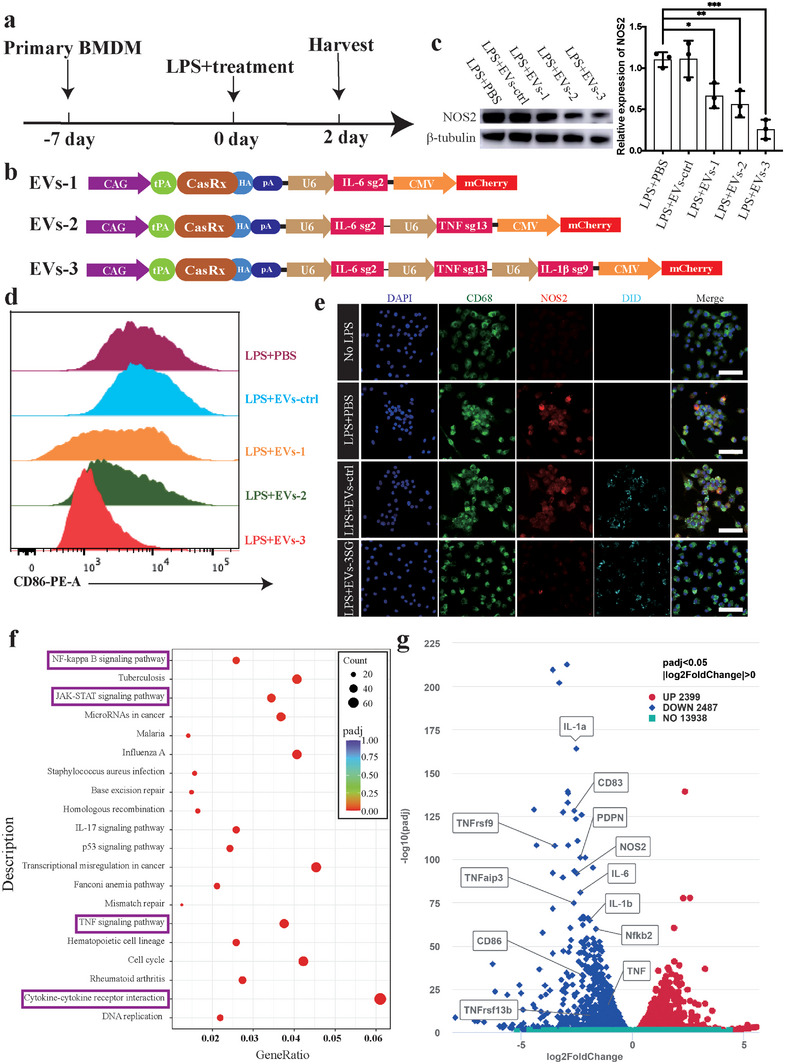
EVs‐3SG inhibit macrophage polarization. a) Schematic illustration of the experimental design used to detect the effectiveness of EVs. b) A schematic of CasRx vectors with a series of different gRNAs targeting cytokines. c) Immunoblotting results showing NOS2 expression levels (left panel). Statistical analysis of NOS2 expression based on the immunoblotting results (right panel). d) Quantification of CD86+ cells showing that the ability to suppress the polarization of macrophages increased from EVs‐1 to EVs‐2 and EVs‐3. e) Immunostaining with DAPI, CD68, NOS2, and DiD showing that EVs‐3SG, but not EVs‐ctrl, inhibited NOS2 expression. Scale bar = 50 µm. f) KEGG signaling pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes showing that the differentially expressed genes were enriched in the inflammatory response pathway, including the NF‐kappa B signaling pathway, JAK‐STAT signaling pathway, TNF signaling pathway and cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction pathway (purple box). g) Volcano plot of the transcriptome showing that the expression levels of typical genes associated with polarization (IL‐6, IL‐1β, TNF, NOS2, CD86, and NF‐κB) were reduced in the EVs‐3SG‐treated group. ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, and *p < 0.05. The data are presented as the means ± SD.
