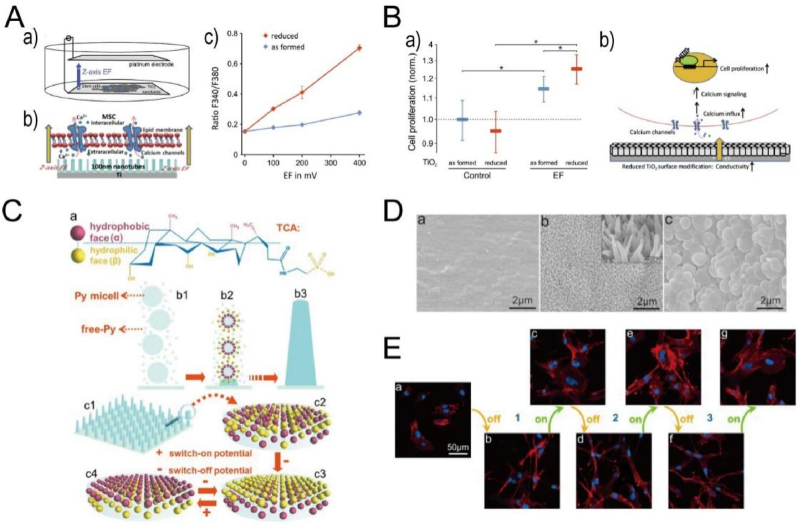
Fig. 17.
(A) Illustration (a) of electric field stimulation of MSC. (b) Schematic diagram of EF-triggered calcium influx. (c) The voltage-dependent elevation of intracellular calcium in as formed and reduced TiO2 after 10 min-EF stimulation [331]. (B) Cell proliferation in reduced and as formed TiO2 nanotubes under EF stimulation: (a) Cell proliferation analysis by WST1 test, and (b) a hypothetical diagram of EF-triggered MSC cell proliferation [331]. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [331]. (C) The chair conformation (a) of TCA. (b) The possible mechanism of preparing 1D NAPPy/TCA (b3). (c) Schematic diagram of the electrical-potential-induced wettability of 1D NAPPy/TCA: c1-c2) the random orientation of TCA without an applied potential, c3) the switch-off state, and c4) the switch-on state [332]. (D) SEM images of NAPPy/TCA prepared in PBS containing 0.01 M (a), 0.07 M (b), and 0.20 M (c) of TCA [332]. (E) Immunofluorescence staining images of MC3T3-E1 cells on 1D NAPPy/TCA in the original state (a), and cycles between switch-off (b, d, and f) and switch-on states (c, e, and g) [332]. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [332].