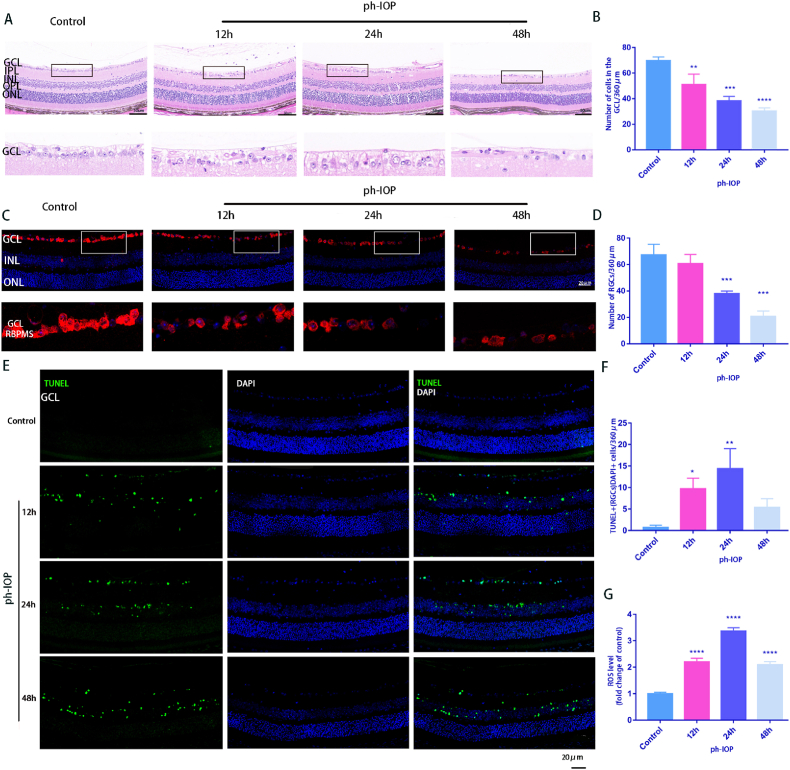
Fig. 4.
ph-IOP injury-induced mitochondrial damage and cell death in RGCs
A: HE-stained retinal sections in control and ph-IOP group at 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h showed retinal structure changes after ph-IOP. Scale bar = 50 μm; The lower pictures are the enlarged representations of the boxed regions of the upper pictures. B: Quantification of the number of cells in the retinal GCL(n = 9); C: RGCs identified using RBPMS antibodies by immunofluorescence with retinal paraffin sections. The lower images are the enlarged representations of the boxed regions of the upper pictures. Scale bar = 20 μm; D: The average number of RGCs at different ph-IOP times (12 h, 24 h, and 48 h) were calculated(n = 9); E: Retinal paraffin sections were stained using TUNEL to observe cell apoptosis. Scale bar = 20 μm; F: TUNEL-positive RGCs were counted(n = 9); G: Retinal ROS generation was determined using DCFH-DA fluorescence intensity quantification after ph-IOP (12 h, 24 h, and 48 h) (n = 9). Values are expressed as the mean ± SD. One-way ANOVA was followed by Dunnett's test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001and****P < 0.0001 vs Control.