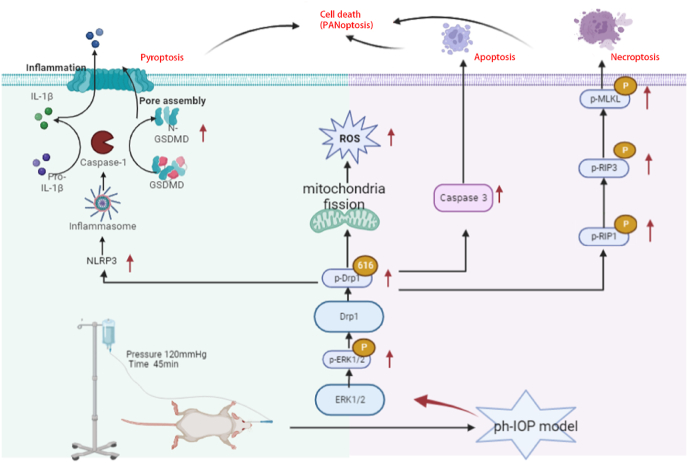
Fig. 9.
ph-IOP -induces the death of RGCs through the ERK1/2-Drp1-ROS signaling pathway
ph-IOP injury is an important pathological process in the development of glaucoma and can aggravate the damage of RGCs in glaucoma. In this study, ph-IOP injury induced the increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2, followed by the phosphorylation of Drp1 at serine 616. This led to mitochondrial fission and dysfunction (decreased mitochondrial membrane potential, decreased ATP, etc.), resulting in the production of large amounts of ROS, eventually leading to the PANoptosis of RGCs. Regulation of Drp1-mediated abnormalities in mitochondrial dynamics is a potential therapeutic target for ph-IOP-induced PANoptosis.