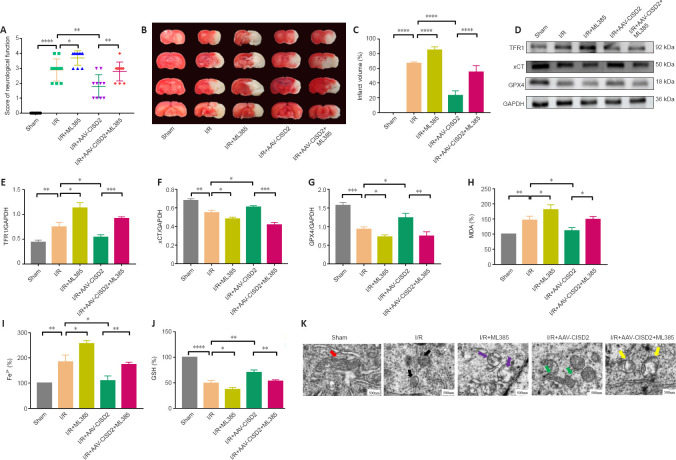
Figure 6.
ML385 reverses CISD2 overexpression-induced neuroprotective effects and resistance to ferroptosis following CIRI.
(A) Neurological dysfunction scores (Longa Score Scale). The effect of ML385 on neurological function in mice following CIRI. (B, C) The effect of ML385 on the infarct volume following CIRI, detected via TTC staining. The volumes of the cerebral infarcts in the I/R + AAV-CISD2 + ML385 group were clearly increased compared with those in the I/R + AAV-CISD2 group. The white area represents the infarct area. The red area represents the normal area. (D–G) Representative western blots and quantitative evaluations of the effect of ML385 on TFR1, xCT, and GPX4 expression in cerebral tissue following CIRI in mice. (H–J) The effect of ML385 on MDA, Fe2+, and GSH in cerebral tissue in mice following CIRI. The data were normalized to that of the control group. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3–10), and were analyzed by a one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test (infarct volume, contents of GSH, MDA, Fe2+, and western blots) or by the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test (neurological dysfunction scores). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. (K) The effect of ML385 on mitochondrial morphology in the cerebral tissue of CIRI mice, examined via TEM. Scale bars: 500 nm. AAV: Adeno-associated virus vector; CIRI: cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury; CISD2: CDGSH iron sulfur domain 2; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; GPX4: glutathione peroxidase 4; GSH: glutathione; I/R: cerebral ischemia/reperfusion; MDA: malondialdehyde; ML385: inhibitor of Nrf2; NC: negative control; TEM: transmission electron microscope; TFR1: transferrin receptor 1; TTC: 2,3,5-triphenyl-2H-tetrazolium chloride; xCT: a cystine/glutamate antiporter.