Abstract
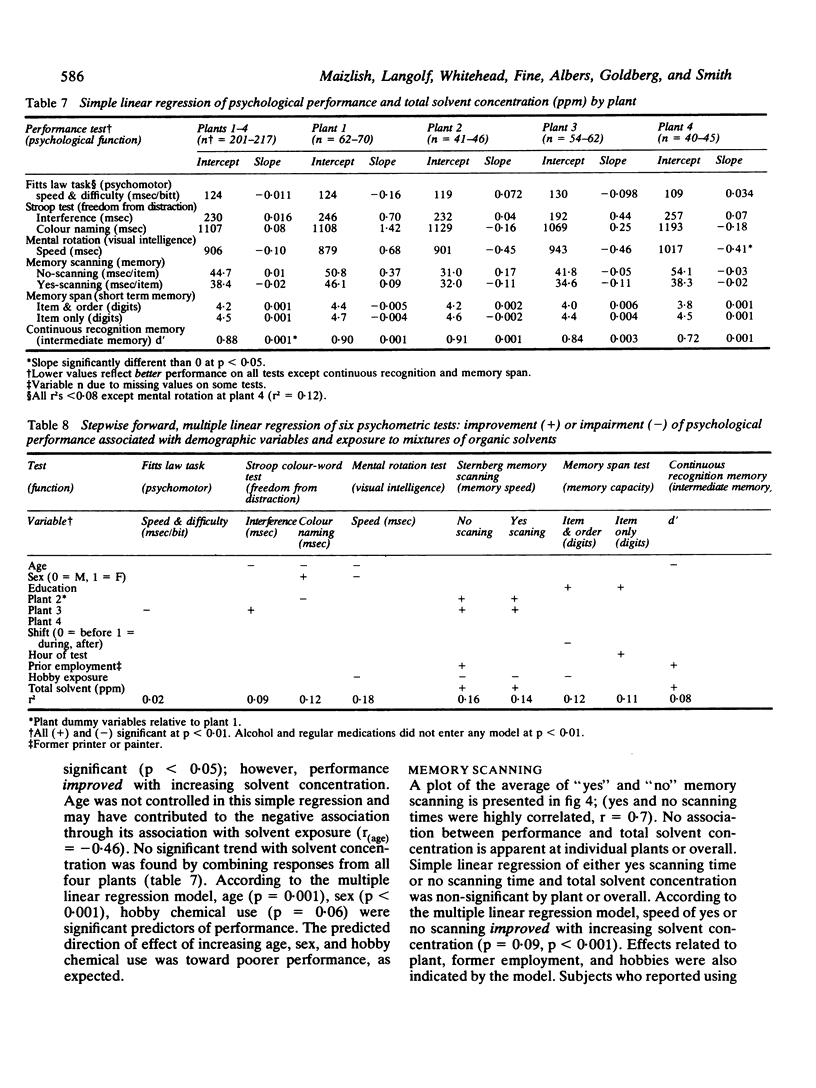
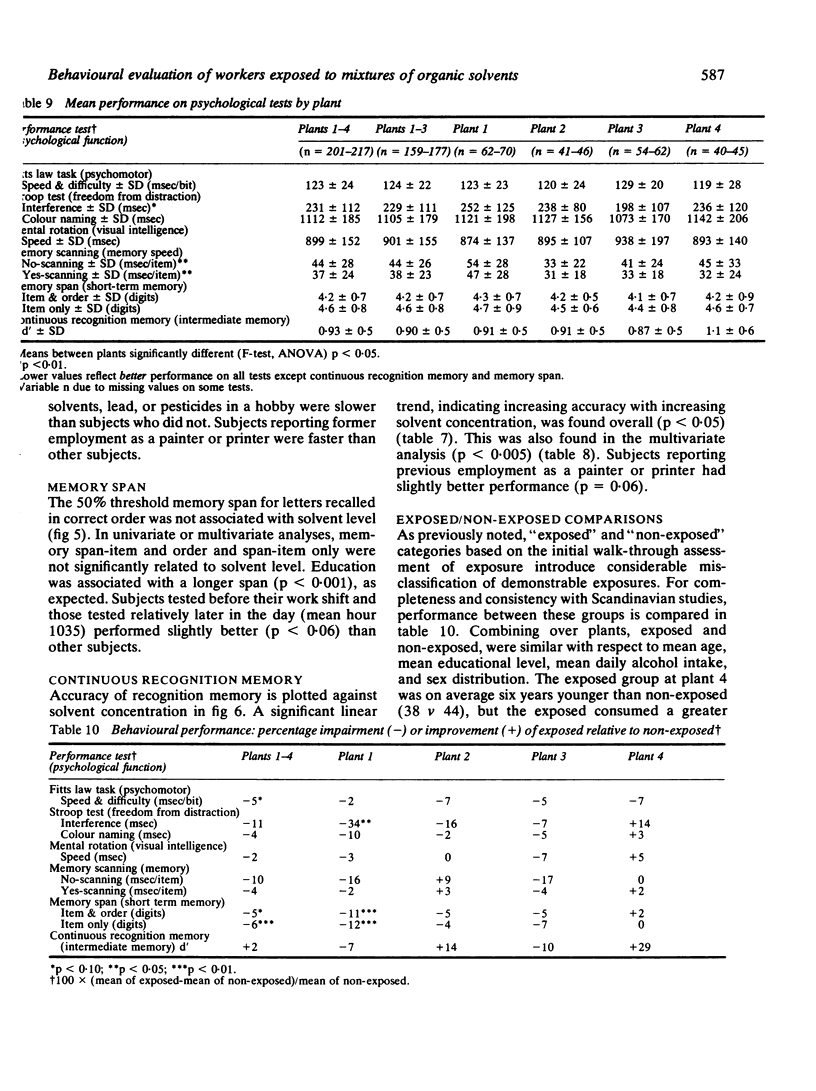
Reports from Scandinavia have suggested behavioural impairment among long term workers exposed to solvents below regulatory standards. A cross sectional study of behavioural performance was conducted among printers and spray painters exposed to mixtures of organic solvents to replicate the Scandinavian studies and to examine dose-response relationships. Eligible subjects consisted of 640 hourly workers from four midwestern United States companies. Of these, 269 responded to requests to participate and 240 were selected for study based on restrictions for age, sex, education, and other potentially confounding variables. The subjects tested had been employed on average for six years. Each subject completed an occupational history, underwent a medical examination, and completed a battery of behavioural tests. These included the Fitts law psychomotor task, the Stroop colour-word test, the Sternberg short term memory scanning test, the short term memory span test, and the continuous recognition memory test. Solvent exposure for each subject was defined as an exposed or non-exposed category based on a plant industrial hygiene walk-through and the concentration of solvents based on an analysis of full shift personal air samples by gas chromatography. The first definition was used to maintain consistency with Scandinavian studies, but the second was considered to be more accurate. The average full shift solvent concentration was 302 ppm for the printing plant workers and 6-13 ppm for the workers at other plants. Isopropanol and hexane were the major components, compared with toluene in Scandinavian studies. Performance on behavioural tests was analysed using multiple linear regression with solvent concentration as an independent variable. Other relevant demographic variables were also considered for inclusion. No significant (p greater than 0.05) relation between solvent concentration and impairment on any of the 10 behavioural variables was observed after controlling for confounding variables. Exposed/non-exposed comparisons showed a significantly poorer digit span among those exposed, but this has not been generally reported in the Scandinavian studies. The medical examination showed no abnormalities of clinical significance. The inability to replicate the findings of the Scandinavian studies could have been due to the shortness of the duration of workers' exposure, the type of solvents in the mixtures, use of different behavioural tests, or to selection factors.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers J. W., Cavender G. D., Levine S. P., Langolf G. D. Asymptomatic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in workers exposed to elemental mercury. Neurology. 1982 Oct;32(10):1168–1174. doi: 10.1212/wnl.32.10.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anshelm Olson B. Effects of organic solvents on behavioral performance of workers in the paint industry. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry N., Waldron H. A., Wells G. G., Wilkinson R. T., Wilson H. K., Jones S. An investigation of the acute behavioural effects of styrene on factory workers. Br J Ind Med. 1980 Aug;37(3):234–240. doi: 10.1136/oem.37.3.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elofsson S. A., Gamberale F., Hindmarsh T., Iregren A., Isaksson A., Johnsson I., Knave B., Lydahl E., Mindus P., Persson H. E. Exposure to organic solvents. A cross-sectional epidemiologic investigation on occupationally exposed care and industrial spray painters with special reference to the nervous system. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1980 Dec;6(4):239–273. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITTS P. M. The information capacity of the human motor system in controlling the amplitude of movement. J Exp Psychol. 1954 Jun;47(6):381–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL A. B. THE ENVIRONMENT AND DISEASE: ASSOCIATION OR CAUSATION? Proc R Soc Med. 1965 May;58:295–300. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M., Axelson O., Blume J., Hogstedt C., Sundell L., Ydreborg B. Psychological function changes among house painters. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1977 Jun;3(2):91–99. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2785. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husman K. Symptoms of car painters with long-term exposure to a mixture of organic solvents. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1980 Mar;6(1):19–32. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen H., Eskelinen L., Husman K., Nurminen M. Behavioral effects of long-term exposure to a mixture of organic solvents. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1976 Dec;2(4):240–255. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iregren A. Effects on psychological test performance of workers exposed to a single solvent (toluene)--a comparison with effects of exposure to a mixture of organic solvents. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol. 1982 Nov-Dec;4(6):695–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A. R., Rohwer W. D., Jr The Stroop color-word test: a review. Acta Psychol (Amst) 1966;25(1):36–93. doi: 10.1016/0001-6918(66)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knave B., Olson B. A., Elofsson S., Gamberale F., Isaksson A., Mindus P., Persson H. E., Struwe G., Wennberg A., Westerholm P. Long-term exposure to jet fuel. II. A cross-sectional epidemiologic investigation on occupationally exposed industrial workers with special reference to the nervous system. Scand J Work Environ Health. 1978 Mar;4(1):19–45. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.2725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savolainen K., Riihimäki V., Linnoila M. Effects of short-term xylene exposure on psychophysiological functions in man. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1979 Nov;44(4):201–211. doi: 10.1007/BF00381655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Langolf G. D., Goldberg J. Effect of occupational exposure to elemental mercury on short term memory. Br J Ind Med. 1983 Nov;40(4):413–419. doi: 10.1136/oem.40.4.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Langolf G. D. The use of Sternberg's memory-scanning paradigm in assessing effects of chemical exposure. Hum Factors. 1981 Dec;23(6):701–708. doi: 10.1177/001872088102300607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


