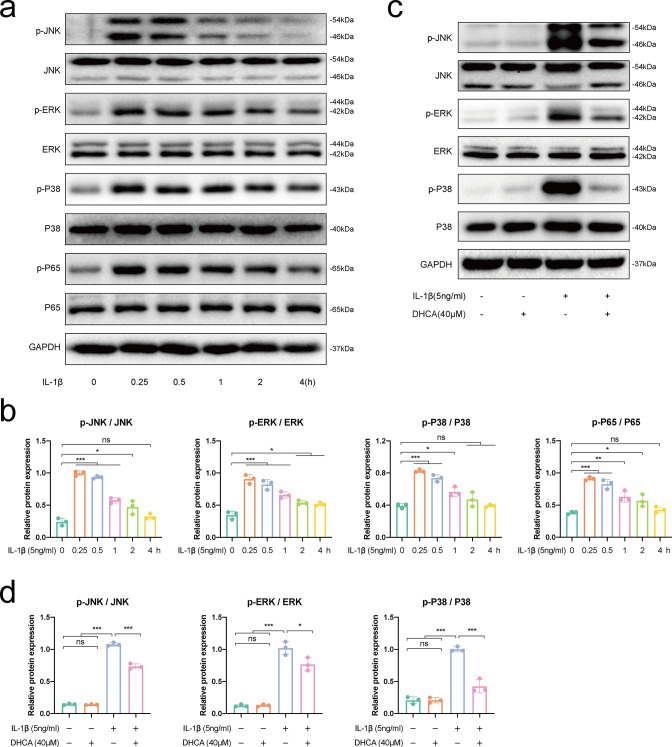
Fig. 6.
The early activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathway induced by interleukin-1β (IL-1β). Chondrocytes were administrated with 5 ng/ml IL-1β at different time durations (0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 hours). a) Western blot bands and b) quantitative analysis of proteins associated with the NF-κB (p-P65, P65) and MAPK (p-JNK, JNK, p-ERK, ERK, p-P38, and P38) pathways. Dihydrocaffeic acid (DHCA) inhibited IL-1β-induced activation of the MAPK signalling pathway. Chondrocytes were treated with 40 μM DHCA for 24 hours or/and 5 ng/ml IL-1β for 0.25 hours. c) Western blot bands and d) quantitative analysis of proteins associated with the MAPK pathway. Data were presented as means and standard deviations (n = 3). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; ns, no significance; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.